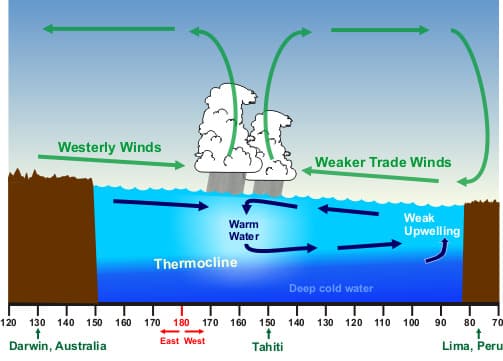
El Niño
An El Niño is a warming of the Pacific Ocean between South America and Papua New Guinea (just north of Australia, an island in the Southwest Pacific). This occurs when the trade winds in that region weaken, which causes the west coast of South America to experience warmer waters. This effect also allows the thermocline to move deeper. This layer of the ocean represents a shallow depth at which a lot of heat is lost. By moving deeper, this demonstrates that the thermocline has receded into the depths and given rise to more warm ocean. This is shown in the image below. El Niño events cause higher precipitation in drier climates on the West Coast but create colder winters in the southeastern US.

La Niña
When a La Niña occurs, it is a cooling of the Pacific Ocean between Papua New Guinea and South America, essentially the opposite of an El Niño. The formation of a La Niña begins when the trade winds get stronger, which pushes warm coastal water further and further away from the South American coastline. Deeper and colder water from the ocean will rise, which is called upwelling. This means that the thermocline has instead moved up, creating less room for warm ocean.
Instead of generally rising temperatures, we see cooler temperatures as well as wet conditions. However, in the southeastern US, we see the opposite, warmer and drier conditions.
Greater Environmental Impacts
An El Niño can have impacts that are shown around the world. The rapid change in climate may cause some species to suffer or require relocation due to their niche not allowing for extremely warm or cold environments. Additionally, migration seasons for birds may change entirely.
On a more global scale, the ocean heat capacity decreases and it is unable to absorb as much energy as needed, which in turn warms the planet. As for the weather, temperature changes will affect precipitations and contribute to either flooding or drought.
🎥 Watch: AP Environmental Science - Earth's Seasons and Climate
Vocabulary
The following words are mentioned explicitly in the College Board Course and Exam Description for this topic.
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| El Niño | A climate phenomenon characterized by warmer than normal ocean surface temperatures in the Pacific Ocean that causes global changes to rainfall, wind, and ocean circulation patterns. |
| El Niño-Southern Oscillation | The coupled ocean-atmosphere system in the tropical Pacific that includes both El Niño and La Niña events and their effects on global climate patterns. |
| La Niña | A climate phenomenon characterized by cooler than normal ocean surface temperatures in the Pacific Ocean that causes global changes to rainfall, wind, and ocean circulation patterns. |
| ocean circulation patterns | The movement and flow of ocean currents and water masses, which can be altered during El Niño and La Niña events. |
| ocean surface temperatures | The temperature of water at the ocean's surface, which changes during El Niño and La Niña events and influences global climate patterns. |
| rainfall patterns | The distribution and amount of precipitation across regions, which can be altered globally during El Niño and La Niña events. |
| wind patterns | The direction and strength of winds across regions, which can be changed globally during El Niño and La Niña events. |
Frequently Asked Questions
What is El Niño and how does it actually work?
El Niño is the warm phase of the El Niño–Southern Oscillation (ENSO). Normally strong Pacific trade winds push warm surface water west, supporting upwelling of cold, nutrient-rich water off Ecuador/Peru and a strong Walker circulation. During El Niño, trade winds weaken or reverse, warm water and the thermocline shift east, upwelling decreases, and Kelvin waves help push warm surface water across the equator. That changes atmospheric circulation (Walker circulation) and creates teleconnections—altered rainfall and storm patterns worldwide (e.g., more rain in western South America, droughts in Australia/Indonesia, collapsed Peruvian fisheries). Key AP terms: sea surface temperature anomalies, thermocline shifts, equatorial upwelling, Kelvin/Rossby waves, Southern Oscillation Index. For the AP exam, link these mechanisms to impacts per ENG-2.C (how ENSO alters rainfall, winds, ocean circulation). Review the topic study guide on Fiveable for diagrams and examples (https://library.fiveable.me/ap-environmental-science/unit-4/el-nino-la-nina/study-guide/xIboNNVBhfU7fegAeCtJ) and try practice questions (https://library.fiveable.me/practice/ap-environmental-science).
What's the difference between El Niño and La Niña?
El Niño and La Niña are opposite phases of the El Niño–Southern Oscillation (ENSO), driven by changes in Pacific sea surface temperatures and the Walker circulation. In El Niño, trade winds weaken or reverse, warm water spreads east across the equatorial Pacific, the thermocline deepens in the east, and upwelling off Peru decreases. That causes increased rainfall in western South America, reduced marine productivity (hurting Peruvian fisheries), and droughts in Australia and Indonesia. La Niña is the reverse: stronger-than-normal trade winds push warm water west, eastern Pacific SSTs are cooler, the thermocline shoals, upwelling increases, boosting fisheries, and you tend to get wetter conditions in Australia/Indonesia and different global teleconnection patterns (e.g., altered storm tracks). Both affect global rainfall, winds, ocean circulation, and are tracked with indices like the Southern Oscillation Index. For AP review, see the Topic 4.9 study guide (https://library.fiveable.me/ap-environmental-science/unit-4/el-nino-la-nina/study-guide/xIboNNVBhfU7fegAeCtJ) and practice questions (https://library.fiveable.me/practice/ap-environmental-science).
Why do El Niño and La Niña only happen in the Pacific Ocean?
Because ENSO depends on a specific set of geographic and atmospheric conditions that are strongest in the equatorial Pacific. The Pacific has a very large, open east–west tropical basin with a warm “western Pacific warm pool” and a strong east–west pressure/temperature gradient. Normal Walker circulation and persistent easterly trade winds push warm surface water west, creating a steep thermocline tilt and strong upwelling off South America. Small changes (weakened trades or Kelvin/Rossby wave propagation) can reverse that pattern, shifting warm water east (El Niño) or making it stronger (La Niña). Other oceans are narrower or have different basin geometry, so they don’t develop the same large-scale thermocline tilt, wave dynamics, or sustained Walker cell that drive ENSO. ENSO events recur every ~2–7 years and are explicitly tied to Pacific sea-surface temperature anomalies and teleconnections (CED: ENG-2.C; EK ENG-2.C.1/2). For a concise AP-aligned review, check the Topic 4.9 study guide (https://library.fiveable.me/ap-environmental-science/unit-4/el-nino-la-nina/study-guide/xIboNNVBhfU7fegAeCtJ) and more unit resources (https://library.fiveable.me/ap-environmental-science/unit-4). Practice ENSO questions at (https://library.fiveable.me/practice/ap-environmental-science).
How do changing ocean temperatures affect weather patterns around the world?
When ocean surface temperatures in the tropical Pacific change (ENSO events), they shift the Walker circulation and trade winds, causing big weather effects worldwide. In El Niño, warm water moves east, the thermocline deepens off South America, and upwelling drops—which collapses Peruvian fisheries and brings increased rainfall to western South America. At the same time, Australia and Indonesia often get droughts. La Niña is basically the opposite: stronger trade winds, cooler eastern Pacific, more upwelling, richer fisheries, and wetter conditions in Australia/Indonesia but drier conditions in parts of the Americas. These shifts create atmospheric teleconnections—altered storm tracks, changes in global rainfall patterns, and variable hurricane activity. For the AP exam, know the mechanisms (sea surface temperature anomalies, thermocline/upwelling, Walker cell) and typical regional impacts. Review the Topic 4.9 study guide on Fiveable for clear examples and practice (https://library.fiveable.me/ap-environmental-science/unit-4/el-nino-la-nina/study-guide/xIboNNVBhfU7fegAeCtJ) and try related practice problems (https://library.fiveable.me/practice/ap-environmental-science).
I'm confused about how El Niño causes droughts in some places but floods in others - can someone explain?
Think of El Niño as the Pacific’s heat and wind pattern flipping: normally strong trade winds push warm water west, so the western Pacific (Indonesia, Australia) has rising air and rains while the east (Peru) is cool and dry. During El Niño the trade winds weaken or reverse, the warm surface water and the convective “warm pool” shift east, and the Walker circulation changes (EK ENG-2.C.1). That shift causes heavy rainfall and flooding in the eastern Pacific and coastal South America while suppressing rainfall—and producing drought—in the western Pacific and parts of Australia/Indonesia (EK ENG-2.C.2). Those changes also alter jet streams and create atmospheric teleconnections, so places far from the tropical Pacific can get wetter or drier depending on the event. For AP review, focus on trade winds, sea surface temperature anomalies, thermocline/upwelling changes, and teleconnections (see the Topic 4.9 study guide: https://library.fiveable.me/ap-environmental-science/unit-4/el-nino-la-nina/study-guide/xIboNNVBhfU7fegAeCtJ). For extra practice, check Fiveable’s APES questions (https://library.fiveable.me/practice/ap-environmental-science).
What causes the ocean surface temperatures to change during El Niño and La Niña events?
El Niño and La Niña change ocean surface temperatures by shifting winds and ocean circulation. Normally strong east-to-west trade winds push warm surface water to the western Pacific, causing upwelling of cold water off South America and a shallow thermocline in the east. During El Niño the trade winds weaken (and Kelvin waves push warm water east), so warm water spreads across the central/eastern Pacific, the thermocline deepens there, and upwelling drops—sea surface temperature anomalies become positive in the east. During La Niña the trade winds strengthen, piling more warm water in the west, shoaling the thermocline in the east, and enhancing cold upwelling—you get negative SST anomalies. These ENSO-driven shifts (Walker circulation changes, Kelvin/Rossby wave effects, altered upwelling) cause the rainfall, wind, and fisheries impacts the AP asks you to describe (ENG-2.C). For a focused review, see the Topic 4.9 study guide (https://library.fiveable.me/ap-environmental-science/unit-4/el-nino-la-nina/study-guide/xIboNNVBhfU7fegAeCtJ) and practice questions (https://library.fiveable.me/practice/ap-environmental-science).
How long do El Niño and La Niña events typically last?
El Niño and La Niña events usually last about 9–12 months, though some episodes can persist for up to 18 months. They typically recur every 2–7 years rather than continuously. On the APES exam you should know these time scales because ENSO timing affects global rainfall, trade winds, upwelling, and fisheries (EK ENG-2.C.1). Shorter/longer durations matter for impacts—e.g., a year-long El Niño can strongly reduce upwelling off Peru, harming fisheries and changing precipitation patterns in Australia and western South America. For more review on causes and effects (Walker circulation, trade winds, sea surface temperature anomalies), see the Topic 4.9 study guide (https://library.fiveable.me/ap-environmental-science/unit-4/el-nino-la-nina/study-guide/xIboNNVBhfU7fegAeCtJ). Need extra practice? Try APES practice problems (https://library.fiveable.me/practice/ap-environmental-science).
Why does El Niño bring more rain to California but droughts to Australia?
During El Niño, trade winds weaken and warm sea-surface-temperature (SST) anomalies shift from the western Pacific toward the central/eastern Pacific. That pushes the zone of rising air and heavy convection (thunderstorms) eastward toward South America and the U.S. West Coast. California sits under those enhanced storm tracks, so it gets more storm systems and rainfall. Meanwhile, Australia and Indonesia lose the warm-pool convection that normally brings them rain; with subsidence (sinking air) replacing rising air there, those regions get reduced precipitation and often drought. This is an ENSO-driven change in the Walker circulation and atmospheric teleconnections—key ideas in ENG-2.C on the APES CED. For a concise review of these mechanisms, see the Topic 4.9 study guide (https://library.fiveable.me/ap-environmental-science/unit-4/el-nino-la-nina/study-guide/xIboNNVBhfU7fegAeCtJ). Practice ENSO questions at Fiveable (https://library.fiveable.me/practice/ap-environmental-science) to prep for exam-style prompts.
What are the main environmental effects of La Niña on global weather?
La Niña = cooler-than-normal sea surface temperatures in the central/eastern tropical Pacific and a stronger Walker circulation. Main environmental effects globally: - Ocean/atmosphere: stronger trade winds, enhanced equatorial upwelling off South America (colder, nutrient-rich water → boosted fisheries). Thermocline shoals in the east, deepens in the west. - Rainfall patterns: wetter than average across Australia, Indonesia, and parts of Southeast Asia; increased flooding risk there. - Drier conditions: often causes drought in the southwestern U.S. and western South America. - Storm/hurricane activity: tends to increase Atlantic hurricane frequency (weaker vertical wind shear) and decrease Pacific hurricane activity. - Teleconnections: shifts in global wind and precipitation patterns that alter ecosystems, agriculture, and fisheries. These points map to CED learning objective ENG-2.C (sea surface temperature anomalies, Walker circulation, teleconnections). For a focused review, see the La Niña study guide (https://library.fiveable.me/ap-environmental-science/unit-4/el-nino-la-nina/study-guide/xIboNNVBhfU7fegAeCtJ) and practice questions (https://library.fiveable.me/practice/ap-environmental-science).
How do scientists predict when El Niño or La Niña events will occur?
Scientists predict El Niño/La Niña by watching ocean–atmosphere signals that the CED lists: sea surface temperature (SST) anomalies, trade-wind strength, thermocline depth, and large-scale waves (Kelvin/Rossby). Key tools: the TAO/TRITON buoy array, satellites (SST and winds), and ocean temperature profiles. They track the Southern Oscillation Index (pressure changes) and rainfall/wind shifts tied to the Walker circulation. Those observations feed coupled ocean–atmosphere computer models that give probabilistic ENSO forecasts (likelihood of El Niño, La Niña, or neutral) weeks to months ahead. Forecasts also use teleconnection patterns to predict global effects like altered upwelling off South America. For AP prep, know the mechanisms (trade winds, upwelling, thermocline, Kelvin/Rossby waves) and how forecasts are made—questions may ask for causes or predicted impacts (e.g., reduced upwelling during El Niño). For a clear review, see the Topic 4.9 study guide (https://library.fiveable.me/ap-environmental-science/unit-4/el-nino-la-nina/study-guide/xIboNNVBhfU7fegAeCtJ). More unit review and practice problems: (https://library.fiveable.me/ap-environmental-science/unit-4) and (https://library.fiveable.me/practice/ap-environmental-science).
I don't understand how ocean temperatures in the Pacific can affect rainfall patterns in completely different continents - how does that work?
Think of the tropical Pacific like a big engine that drives global air circulation. In normal years strong trade winds push warm surface water west, keeping the eastern Pacific cool and fueling rising air (rain) over the western Pacific. During El Niño the ocean surface temperature anomalies shift eastward, weakening the Walker circulation and changing where air rises and sinks. That shifts major wind patterns and the jet stream—atmospheric teleconnections—so places far from the Pacific get more or less moisture. For example, western South America gets increased rainfall and Peru’s upwelling (and fisheries) decline, while Australia and Indonesia can get drought. La Niña is the opposite: stronger trade winds, stronger upwelling, and opposite rainfall changes. This is exactly what the CED expects you to know for ENG-2.C (El Niño/La Niña affect global rainfall, winds, and ocean circulation). For a focused review, check the Topic 4.9 study guide (https://library.fiveable.me/ap-environmental-science/unit-4/el-nino-la-nina/study-guide/xIboNNVBhfU7fegAeCtJ).
What geological and geographic factors influence El Niño and La Niña patterns?
El Niño and La Niña are driven by ocean–atmosphere interactions, but geology and geography shape how they play out. Geographic factors: the width/depth of the tropical Pacific basin, position of the equator, and continental coastlines (especially western South America) control where warm water can pile up or where cold deep water can upwell. Coastal geometry and shallow continental shelves (Peru) make upwelling during normal conditions strong—El Niño suppresses that upwelling. Atmospheric geography (Walker circulation and trade-wind strength across the equatorial Pacific) links to sea surface temperature anomalies and thermocline shifts. Geological/topographic factors: seafloor features and basin depth affect propagation of Kelvin and Rossby waves that move heat east–west, and plate boundary/subduction zones influence coastal relief and current patterns. On the AP exam, focus on how these factors change upwelling, rainfall, and global teleconnections (ENG-2.C). Review this topic study guide for targeted practice (https://library.fiveable.me/ap-environmental-science/unit-4/el-nino-la-nina/study-guide/xIboNNVBhfU7fegAeCtJ) and hit practice problems at (https://library.fiveable.me/practice/ap-environmental-science).
How do El Niño and La Niña affect ocean circulation patterns besides just temperature?
Beyond changing sea-surface temperature, El Niño and La Niña reorganize ocean circulation in several key ways. They alter the Walker circulation and the strength/direction of the trade winds, which changes east–west surface currents along the equator. That drives Kelvin and Rossby waves that shift the thermocline (deeper in El Niño, shallower in La Niña), so equatorial upwelling off South America is suppressed during El Niño and enhanced during La Niña. Those changes change nutrient supply, coastal productivity, and fisheries. ENSO also produces atmospheric teleconnections that modify wind stress and hence mid-latitude surface currents and storm tracks, so ocean gyres and regional circulation patterns can shift. For AP exam connections, link these effects to EK ENG-2.C.1 (rainfall, wind, ocean circulation) and use terms like Walker circulation, trade winds, thermocline, upwelling, Kelvin/Rossby waves. Review this topic on Fiveable’s study guide (https://library.fiveable.me/ap-environmental-science/unit-4/el-nino-la-nina/study-guide/xIboNNVBhfU7fegAeCtJ) and practice questions (https://library.fiveable.me/practice/ap-environmental-science).
Why do some regions experience opposite effects during El Niño versus La Niña events?
El Niño and La Niña are opposite phases of ENSO, so they flip wind, ocean, and pressure patterns—that’s why places get opposite effects. In normal/La Niña conditions, strong east-to-west trade winds pile warm water in the western Pacific, a steep thermocline, and lots of upwelling and cool nutrient-rich water off South America. That gives wet Australia/Indonesia and dry South America. During El Niño, weakened trade winds let warm surface water spread east, flatten the thermocline, reduce upwelling off Peru, and shift the Walker circulation and atmospheric convection eastward. So western Pacific dries while eastern Pacific gets more rain. Those shifts travel as atmospheric teleconnections, changing rainfall and storms far from the Pacific. For AP exam connections, focus on trade winds, Walker circulation, thermocline/upwelling, and teleconnections (see the Topic 4.9 study guide on Fiveable for review) (https://library.fiveable.me/ap-environmental-science/unit-4/el-nino-la-nina/study-guide/xIboNNVBhfU7fegAeCtJ). For extra practice, try the unit practice questions (https://library.fiveable.me/practice/ap-environmental-science).
What's the connection between trade winds and El Niño/La Niña cycles?
Trade winds are the engine of ENSO. Normally they blow west across the equatorial Pacific, pushing warm surface water into the western Pacific and strengthening the Walker circulation. That piling of warm water raises sea surface temps in the west, causes a shallow thermocline in the east, and drives upwelling of cold, nutrient-rich water off South America. In El Niño, those trade winds weaken or reverse. Warm water sloshes east, the eastern thermocline deepens, upwelling drops, and you get warmer SSTs, more rainfall in western South America, and droughts in Australia/Indonesia—big impacts on fisheries and global weather (EK ENG-2.C.1/2). In La Niña, trade winds strengthen, enhancing westward flow, cooling the eastern Pacific, increasing upwelling, and shifting rainfall patterns the opposite way. For AP review, remember Walker circulation, thermocline shifts, Kelvin/Rossby wave effects. See the topic study guide (https://library.fiveable.me/ap-environmental-science/unit-4/el-nino-la-nina/study-guide/xIboNNVBhfU7fegAeCtJ) and more practice problems (https://library.fiveable.me/practice/ap-environmental-science).