Political Processes
Political maps have changed over time due to a variety of factors, including shifts in political boundaries, the formation of new countries, and changes in the names or borders of existing countries.
Throughout history, political boundaries have often changed as a result of wars, conquests, and other types of political conflict. For example, the borders of many European countries have changed significantly over the past several centuries as a result of wars and treaties.
Political boundaries have also changed as a result of the formation of new countries. For example, the breakup of the Soviet Union in the 1990s led to the formation of several newly independent countries in Eastern Europe and Central Asia.
In addition to changes in political boundaries, the names and borders of existing countries have also changed over time. For example, the name of the country known as Ceylon changed to Sri Lanka in 1972, and the country of Burma changed its name to Myanmar in 1989.
Overall, the political map has changed dramatically, even in just the last century. But for a real eye opener, take a look at what the political map looked like in 1800.
So how did we go from that to what we have now? Well, it was a messy process as there are forces at play that can unify or break up countries.
The idea that nations could establish an independent country is not all that old. In the 1600s, during the Enlightenment, nationalism was first theorized. Nationalism is a political and social ideology that emphasizes the collective identity and interests of a nation or a people. It involves a belief in the right of a particular nation or group to self-determination, and often involves the promotion of national unity, pride, and culture. This is the spark that leads to an independent nation state. Although too much of it can also be detrimental to a state and can lead to never ending wars, as we saw in the 19th and 20th centuries.

Colonialism & Imperialism
Throughout history, the political map was vastly altered because of imperialism. Imperialism is the practice of a country extending its power and influence over other countries, typically through the use of military force, economic coercion, or cultural domination. It often involves the colonization or annexation of other countries, and the exploitation of their resources and labor for the benefit of the imperial power. This could be politically, culturally, or economically. States are motivated to practice imperialism for two reasons - materials and markets. Imperialism increases access to natural resources and creates new markets to sell goods.
Colonialism is the practice of a country establishing and maintaining colonies in other parts of the world, typically for the purpose of economic exploitation, cultural assimilation, or political control. It involves the settlement of a colony by citizens of the colonizing country, and the imposition of the colonizing country's culture, laws, and governance on the colonized territory. The Europeans began practicing colonialism in the 1500s and expanded rapidly until much of the world was colonized by Europeans.
Spain and Portugal kicked things off in the 1500s by establishing empires in Central and South America for “God, Glory, and Gold.” ("God, Glory, Gold" is a phrase that is often associated with the Age of Exploration, a period in history during which European powers embarked on voyages of discovery and conquest around the world.) England, France, and the Netherlands followed, mostly colonizing different territories in North America. The early Europeans fought each other frequently for more dominance across the Americas straight through the 1800s.
Berlin Conference
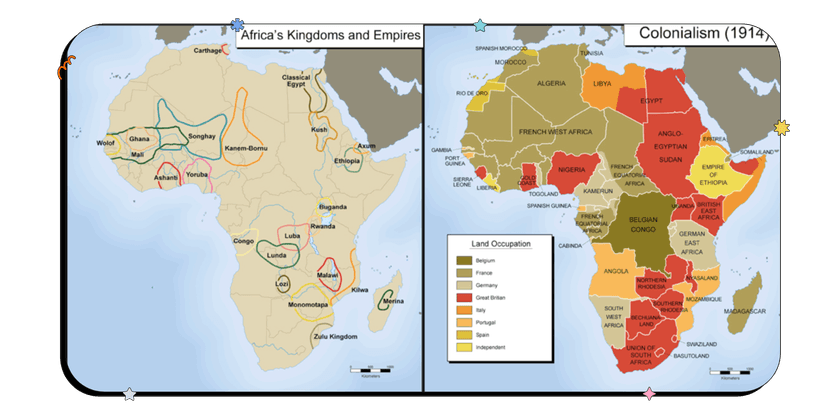
In the late 1800s, Germany, Belgium, Italy, and others joined the game, setting their sights on Africa and Asia to catch up with their European competitors. By the end of the 1800s, all of Europe turned to Africa and European leaders met at the Berlin Conference (without any African leaders present) to divide up the continent. They didn’t pay any attention to tribal and traditional boundaries, and instead, completely redrew country borders however they wanted.
Here’s what Africa looked like before and after the Berlin Conference. Notice how afterward, only Ethiopia and Liberia remained independent. Keep in mind that native Africans lived across the continent before Europeans arrived and they had established centuries of flourishing empires, cultures, and societies. European colonization changed all of that.
World Wars
Both World War I and II led to drastic changes in the appearance of the political map.
World War 1
World War 1 was a global conflict that took place from 1914 to 1918. It was sparked by the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria-Hungary, and quickly escalated into a full-scale war involving many of the major powers of the time.
The main Allied powers in World War 1 were France, Russia, and the United Kingdom, who were joined by the United States in 1917. The main Central powers were Germany, Austria-Hungary, and the Ottoman Empire.
World War 1 was characterized by the use of modern industrial and technological advances, such as machine guns, poison gas, and tanks, which resulted in a high number of casualties. It also saw the first use of aircraft in warfare, and the development of new forms of warfare, such as trench warfare and total war.
The war had a significant impact on global politics, and led to significant changes in the balance of power and the political landscape in Europe and beyond. It also set the stage for the even more devastating World War 2, which took place just two decades later.
After World War I, new states were carved out of the losing belligerents including the Ottoman Empire, Austria-Hungary, and Germany. Rising nationalism also triggered independence in other countries at the same time including Ireland from the United Kingdom and Latvia, Estonia, and Lithuania from Russia.
World War 2
World War 2 was a global conflict that took place from 1939 to 1945. It was sparked by the invasion of Poland by Nazi Germany, and quickly escalated into a full-scale war involving many of the major powers of the world.
The main Allied powers in World War 2 were the United States, the United Kingdom, the Soviet Union, and China, who were joined by many other countries. The main Axis powers were Nazi Germany, Fascist Italy, and Imperial Japan.
World War 2 was a total war, involving the mobilization of entire societies for the war effort. It saw the use of advanced technological and military innovations, such as nuclear weapons, and resulted in a high number of casualties.
The war had a significant impact on global politics, and led to significant changes in the balance of power and the political landscape in Europe and beyond. It also set the stage for the Cold War, a period of political and military tension that lasted for more than four decades.
During World War II, the rapid expansion of the Nazis and Imperial Japan changed the maps of Europe and Asia. As soon as both powers were defeated in 1945, their short lived empires were broken up or occupied by other states. For example, the states of Eastern Europe went from Nazi occupation to Soviet control and remained part of the Soviet Union until 1991.
The Cold War
The Cold War (1945-1991) was a period of political and military tension that lasted from the late 1940s until the early 1990s. It was characterized by a global power struggle between the United States and the Soviet Union, and their respective allies, who were divided by ideological differences and competing interests.
The Cold War was fueled by the emergence of two superpowers after World War II, the United States and the Soviet Union, who were each determined to spread their own ideology and influence around the world. The two sides engaged in a variety of proxy wars, arms races, and other forms of competition, but never directly confronted each other in open warfare.
The Cold War had a significant impact on global politics, and shaped the course of international relations for more than four decades.
The US focused on economic imperialism in Latin America and adopted old colonies as new states including Hawaii and Alaska. Meanwhile, the Soviets were pressing into Asia, which prompted the US to fight back. Proxy Wars were fought in Korea, Vietnam, and Afghanistan as the superpowers fought each other through the peoples of these countries.
Decolonization
The end of World War II also ushered in an era of decolonization. Decolonization is the process of a colony gaining independence and becoming a sovereign nation. It involves the withdrawal of a colonizing power from a colonized territory, and the transfer of political and economic control to the people of the colony.
States under colonization fought for their independence from the moment they were occupied. But the World Wars stalled any independence efforts and the colonized nations were forced to join their colonizers in the fight. This is what made these wars global in the first place. Australians, Indians, Brazilians, and Egyptians found themselves entangled in the web of alliances.
After World War II, the independence movements recommenced almost immediately. The European nations were severely weakened by the war and did not have the resources to retain control over their colonies. Some countries like France fought hard to hang on to colonies, but Vietnam, Indonesia, and Algeria fought back and won their independence.
The British were in ruins after the war and agreed to a peaceful independence for India and Israel. However, both countries were quickly thrown into violent conflict as India was partitioned to also create Pakistan and as Israel was attacked by every surrounding country.
Post-Cold War
In the 1990s, the Soviet Union collapsed, which led to the independence of 15 new countries in a single year. The quick shift of power was actually peaceful because the Soviets were so weakened by the costly war against Afghanistan that they had fought for a decade.
The geopolitical forces of nationalism and imperialism changed the map dramatically in the last two hundred years and both of these forces continue to affect current issues. Within the next century, the map will surely change further as more countries gain independence.
🎥 Watch: AP HUG - Supranationalism
Vocabulary
The following words are mentioned explicitly in the College Board Course and Exam Description for this topic.
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| colonialism | The practice of establishing political and economic control over distant territories and their populations, typically involving settlement and resource extraction. |
| devolution | The transfer of political power and authority from a central government to regional or local governments. |
| imperialism | The policy or practice of extending a country's power and influence over other territories and peoples through military, political, or economic means. |
| independence movements | Organized efforts by colonized or subjugated peoples to achieve political autonomy and self-governance. |
| nation-states | Political entities in which the boundaries of the state align with the territory of a nation, creating a close match between political and cultural identity. |
| political boundaries | Lines that divide territory and establish the limits of political jurisdiction and sovereignty between states or political entities. |
| self-determination | The right of a people to choose their own form of government and determine their political status without external control. |
| sovereignty | The authority of a state to govern itself and make independent decisions without external interference. |
Frequently Asked Questions
What is sovereignty and why does it matter for countries?
Sovereignty is a state’s legal and political authority to control its territory, make and enforce laws, and be recognized by other states. It matters because sovereignty defines who has the final say inside borders (laws, resources, taxes, security) and who speaks for that territory internationally. Weak or contested sovereignty leads to issues the CED highlights—self-determination, devolution, colonialism/independence movements, and boundary disputes—because groups may seek autonomy or outside recognition. On the AP exam, you’ll need to explain how sovereignty interacts with processes like devolution or imperialism (EK PSO-4.B.1). Sovereignty also shapes things like control of an exclusive economic zone, joining supranational unions, and reactions to secessionist movements. For more review on political processes, see the Topic 4.2 study guide (https://library.fiveable.me/ap-human-geography/unit-4/political-processes/study-guide/9WmdRJEK49Nh0Nu95fLs) and practice questions (https://library.fiveable.me/practice/ap-human-geography).
How did colonialism shape the borders we see on maps today?
Colonialism shaped today’s borders by forcing European ideas of sovereignty and statehood onto places that already had different ethnic, linguistic, or political landscapes. During imperialism, Europeans drew straight lines or arbitrary borders (superimposed boundaries)—think the Berlin Conference in Africa—with little regard for existing nations or self-determination. That produced many multinational states, minority groups split across borders (irredentism), and later independence movements and decolonization that sometimes led to partition (e.g., India/Pakistan). Those historical processes explain why some boundaries cause ongoing conflict, devolution pressures, or calls for autonomous regions. For AP exam relevance, the CED lists colonialism and the Berlin Conference under EK PSO-4.B.2 and even appears in practice questions (Unit 4). Review Topic 4.2 on Fiveable (study guide: https://library.fiveable.me/ap-human-geography/unit-4/political-processes/study-guide/9WmdRJEK49Nh0Nu95fLs) and practice problems (https://library.fiveable.me/practice/ap-human-geography) to see examples and sample questions.
What's the difference between a nation and a state - I'm so confused?
Short answer: a state is a political entity with defined territory, a permanent population, a government, and sovereignty (the authority to make and enforce laws). A nation is a group of people who share a common identity—culture, language, religion, or history. They’re different things but often overlap. Examples that help: Japan is often called a nation-state (one dominant nation in one sovereign state). The Kurds are a nation (shared identity) without an independent state—so they push for self-determination. Multinational states (like India) contain many nations under one sovereign state, which can cause devolutionary pressures (ETHNIC divisions, autonomy demands). For AP exam terms, remember sovereignty, nation-state, and self-determination (CED EK PSO-4.B.1). If you want a quick Topic 4.2 review, check the Fiveable study guide (https://library.fiveable.me/ap-human-geography/unit-4/political-processes/study-guide/9WmdRJEK49Nh0Nu95fLs) and practice questions (https://library.fiveable.me/practice/ap-human-geography).
Why did European countries want to colonize other places in the first place?
European states colonized for a mix of economic, political, and ideological reasons that shaped modern political geography. Economically, they wanted raw materials, new markets, and land for investment and settlement. Politically, states sought strategic ports, naval bases, and prestige—growing national power and competing with rivals (imperialism). Ideologically, ideas like “civilizing” missions and nationalism justified colonial control and influenced concepts of sovereignty and nation-states. Technology (steamships, medicine, weapons) and administrative tools made overseas control easier. Events like the Berlin Conference (1884–85) show how Europeans formalized boundaries and superimposed states, creating many contemporary borders and independence movements studied in Topic 4.2. For AP prep, focus on how colonialism, imperialism, decolonization, and self-determination changed boundaries (see the Topic 4.2 study guide: https://library.fiveable.me/ap-human-geography/unit-4/political-processes/study-guide/9WmdRJEK49Nh0Nu95fLs). For unit review and practice problems, check the Unit 4 overview (https://library.fiveable.me/ap-human-geography/unit-4) and the 1,000+ practice items (https://library.fiveable.me/practice/ap-human-geography).
Can someone explain self-determination in simple terms?
Self-determination means a group of people (usually sharing a common culture, language, or history) have the right to choose their own political status—like forming their own nation-state, gaining autonomy, or deciding who governs them. It ties directly to sovereignty and independence movements: people use self-determination to justify breaking away from empires or states (decolonization and secession) or to demand autonomous regions instead of full independence. On the AP Human Geography exam this shows up under political processes (PSO-4.B and EK PSO-4.B.1)—know how self-determination links to colonialism, devolution, and nation-state formation. For a quick review, check the Topic 4.2 study guide (https://library.fiveable.me/ap-human-geography/unit-4/political-processes/study-guide/9WmdRJEK49Nh0Nu95fLs). For extra practice, use Fiveable’s practice questions (https://library.fiveable.me/practice/ap-human-geography).
What caused all the independence movements after World War II?
After WWII a few big forces drove independence movements: weakened European powers (economic cost and loss of legitimacy after the war), rising ideas of self-determination and nation-state sovereignty, and stronger anti-colonial nationalism in colonies. The war also spread political ideas (through soldiers, media, and the UN) and created power vacuums—plus Cold War rivalry gave both the US and USSR incentives to support decolonization or local movements. Colonialism and imperialism had created boundaries and inequalities that made colonies want independence; decolonization was the process that followed. These causes map directly to EK PSO-4.B.1–4.B.2 in the CED and are commonly tested in Unit 4 free-response prompts. For a concise review, see the Topic 4.2 study guide (https://library.fiveable.me/ap-human-geography/unit-4/political-processes/study-guide/9WmdRJEK49Nh0Nu95fLs) and try practice questions (https://library.fiveable.me/practice/ap-human-geography).
How is devolution different from just regular independence movements?
Devolution is when a central government grants—or loses—some political power to regional or local authorities within the same state (like creating autonomous regions), while an independence movement seeks full sovereignty and separation to form a new state. Devolution is a form of internal rearrangement of power (a centrifugal/centripetal issue in PSO-4.B), often used to reduce conflict by giving self-determination without changing international borders. Independence movements push beyond that, aiming to change boundaries and statehood (decolonization or secession). On the AP exam, be ready to connect devolution to multinational states, ethnic nationalism, and uneven development as centrifugal forces (see FRQ prompts in Topic 4.2). For review, check the Topic 4.2 study guide on Fiveable (https://library.fiveable.me/ap-human-geography/unit-4/political-processes/study-guide/9WmdRJEK49Nh0Nu95fLs) and more unit resources (https://library.fiveable.me/ap-human-geography/unit-4) or practice questions (https://library.fiveable.me/practice/ap-human-geography).
I don't understand how imperialism actually worked - can someone break it down?
Imperialism = when powerful states extended control over weaker places to get resources, markets, strategic land, and prestige. It usually happened in stages: explorers/companies claimed territory → missionaries and traders set up posts → governments sent troops and formalized control (laws, governors, railroads) → colonizers changed local economies and borders. Technology (steamships, guns, medicine) and mapmaking made it easier. European powers often drew borders with little regard for ethnic groups (superimposed boundaries from the Berlin Conference, 1884–85), which later caused conflicts and independence movements. Over time colonized people pushed for self-determination; decolonization and nationalist movements led to new sovereign states, sometimes with partition or irredentism. For AP HUG, know the links between colonialism/imperialism, sovereignty, and boundary types—these show up on multiple-choice and FRQs (e.g., superimposed boundaries). Review Topic 4.2 study guide (https://library.fiveable.me/ap-human-geography/unit-4/political-processes/study-guide/9WmdRJEK49Nh0Nu95fLs), the Unit 4 overview (https://library.fiveable.me/ap-human-geography/unit-4), and practice questions (https://library.fiveable.me/practice/ap-human-geography) to prep.
What are some examples of countries that got independence through self-determination?
Self-determination led to many countries’ independence in the 20th century—usually as colonies pushed to form sovereign nation-states. Clear examples: India (1947, end of British rule and creation of nation-states after independence/partition), Ghana (1957, first Sub-Saharan African colony to gain independence through nationalist pressure), Algeria (1962, independence from France after a prolonged nationalist war and a self-determination referendum), Kenya (1963, end of British colonial rule after nationalist movements), and the Philippines (1946, U.S. granted independence after Filipino self-rule movements). These fit CED ideas: decolonization, independence movements, sovereignty, and self-determination (EK PSO-4.B.1 & EK PSO-4.B.2). For more AP-aligned examples and practice, check the Topic 4.2 study guide (https://library.fiveable.me/ap-human-geography/unit-4/political-processes/study-guide/9WmdRJEK49Nh0Nu95fLs), the Unit 4 overview (https://library.fiveable.me/ap-human-geography/unit-4), and practice questions (https://library.fiveable.me/practice/ap-human-geography).
How do I write an essay about how colonialism affected modern political boundaries?
Start with a clear thesis that answers how colonialism shaped today’s political boundaries (e.g., “European colonialism produced many superimposed borders that often ignored ethnic groups, creating long-term sovereignty and devolution challenges”). Use 2–3 concrete case studies (Africa—Berlin Conference, South Asia—1947 partition, Middle East—mandates) and label the processes with AP terms: colonialism, imperialism, partition, superimposed boundaries, decolonization, self-determination, irredentism, and devolution. For each case give one short cause (how colonizers drew borders) and one short effect (ethnic conflict, weak nation-state, boundary disputes). Connect to contemporary concepts like sovereignty and nation-state. Conclude by linking colonial legacy to modern boundary delimitation/demarcation problems. On the exam, write 5–7 concise paragraphs, use geographic evidence (maps or examples), and directly answer the prompt to earn full FRQ points. Review Topic 4.2 for key examples (study guide: https://library.fiveable.me/ap-human-geography/unit-4/political-processes/study-guide/9WmdRJEK49Nh0Nu95fLs) and practice FRQs (https://library.fiveable.me/practice/ap-human-geography).
Why do some ethnic groups want their own countries instead of staying in bigger states?
Often ethnic groups want their own country because they seek self-determination—political control over their territory, culture, and laws. Ethnic differences can be centrifugal: if a group feels politically marginalized, economically neglected (uneven development), or threatened culturally, they may push for independence, irredentism, or an autonomous region. Historical processes like colonialism and partition also create multinational states where borders don’t match ethnic boundaries, so independence movements arise to form nation-states that align sovereignty with a single ethnic nation. Communication tech and nationalism help organize these movements, while governments may respond with devolution or repression. This ties directly to Topic 4.2 (EK PSO-4.B.1–2) on sovereignty, nation-states, and devolution—stuff you’ll see on the AP exam. For a quick refresher, check the Topic 4.2 study guide (https://library.fiveable.me/ap-human-geography/unit-4/political-processes/study-guide/9WmdRJEK49Nh0Nu95fLs) and more unit review (https://library.fiveable.me/ap-human-geography/unit-4). Practice questions are at (https://library.fiveable.me/practice/ap-human-geography).
What's the connection between nationalism and the creation of new countries?
Nationalism is a powerful fuel for the creation of new countries because it ties shared identity (language, religion, history) to the political goal of self-determination. When a group’s national identity clashes with existing state boundaries or feels denied political power, nationalism becomes a centrifugal force that sparks independence movements, decolonization, or partition (CED EK PSO-4.B.1–4.B.2). Those movements challenge sovereignty and can produce new nation-states (or autonomous regions) after processes like negotiation, conflict, or international recognition. Examples on the exam often link nationalism to boundary changes (e.g., partition, irredentism), so be ready to explain causes and outcomes for free-response prompts (Topic 4.2/PSO-4.B). For targeted review, see the Topic 4.2 study guide (https://library.fiveable.me/ap-human-geography/unit-4/political-processes/study-guide/9WmdRJEK49Nh0Nu95fLs), the Unit 4 overview (https://library.fiveable.me/ap-human-geography/unit-4), and practice FRQs (https://library.fiveable.me/practice/ap-human-geography).
Did decolonization actually solve the problems that colonialism created?
Short answer: not completely. Decolonization did give many places sovereignty, nation-states, and formal self-determination—but it didn’t magically fix problems colonialism created. Colonial powers often left superimposed boundaries (Berlin Conference, partitions) that ignored ethnic geography, which fuelled devolution, irredentism, and conflict. Economic ties and unequal development persisted—former colonies often faced weak institutions, single-commodity economies, and neo-colonial dependency. Some states built stable governments and development; others struggled with ethnic violence, border disputes, and poverty. For AP exam focus: link these outcomes to EK PSO-4.B (colonialism, independence movements, devolution) and use examples of superimposed boundaries or partition in free-response answers. Review Topic 4.2 for targeted examples (https://library.fiveable.me/ap-human-geography/unit-4/political-processes/study-guide/9WmdRJEK49Nh0Nu95fLs) and practice applying terms on the unit page (https://library.fiveable.me/ap-human-geography/unit-4) or with practice problems (https://library.fiveable.me/practice/ap-human-geography).
How did the concept of nation-states spread around the world?
The nation-state idea spread mainly through European imperialism and colonialism from the 17th–20th centuries. European powers exported concepts of sovereignty, fixed borders, and the nation-state when they carved up Africa at the Berlin Conference, partitioned empires (like British India in 1947), and imposed administrative boundaries on colonies. Decolonization and independence movements after World War II then used the idea of self-determination to create new states—some aligned with a single national identity, many didn’t, which later caused devolution, irredentism, and border disputes. Today the nation-state model is global but imperfect: sovereignty remains central, yet multinational states and supranational bodies (EU) complicate it. This is a core AP Human Geography topic (Topic 4.2) and shows up in both multiple-choice and free-response questions—review the concepts and examples in the Topic 4.2 study guide (https://library.fiveable.me/ap-human-geography/unit-4/political-processes/study-guide/9WmdRJEK49Nh0Nu95fLs) and practice related questions (https://library.fiveable.me/practice/ap-human-geography).
I missed class - what exactly is devolution and can you give me examples?
Devolution is the transfer of political power from a central government to subnational or regional authorities—usually to give a group more self-determination while the state keeps sovereignty. It’s a centrifugal process tied to ethnicity, nationalism, or uneven development (CED keywords: sovereignty, nation-state, self-determination, multinational state). Examples: Scotland’s push for autonomy and its 2014 independence referendum; Catalonia’s independence movement in Spain; the breakup of Yugoslavia and the Soviet Union (full state collapse, extreme devolution/independence); and autonomy arrangements like Northern Ireland or federal vs. unitary tensions. On the AP exam, devolution appears in free-response prompts about centrifugal forces and multinational states (see FRQ #1 in the CED). Review this topic’s essential knowledge and examples in the Topic 4.2 study guide (https://library.fiveable.me/ap-human-geography/unit-4/political-processes/study-guide/9WmdRJEK49Nh0Nu95fLs) and practice more questions at (https://library.fiveable.me/practice/ap-human-geography).
