A greying population can be a sign of trouble:
A number of countries have a high percentage of people that are in or near retirement age (60 or older). This can happen for a number of reasons and have some serious consequences in those regions.
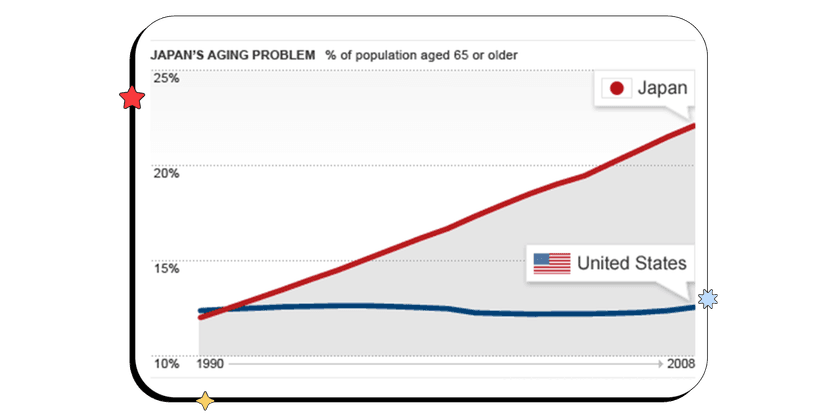
Countries that are in stages four and five of the demographic transition model have lower birth rates, but higher death rates than countries in stages two and three. Less people are in their childbearing years. These countries tend to have more women who are educated. For these reasons, the birth rates are lower.
With better health care more people are living into their 70s and 80s, but this causes the death rate to rise, because of the large number of older people. When these countries are in stage five of the DTM, they have a negative natural increase rate, which means their populations are decreasing.
Countries that are in stages four and five are more developed and therefore have long life expectancies.
Political Consequences
There are political consequences because older people tend to vote more. They also are more concerned about health care issues, because it more directly affects them. With the older population voting more, the policies that the government puts in place would more likely apply to this age group.
Therefore, politicians need to garner support from older people, handle issues like health care more directly, and possibly even have more elderly in office.

Social Consequences
There are also social consequences. Besides health care, things like housing for the older generations need to be addressed. Countries with older populations need to invest in retirement homes and have more people to help care for the elderly.
Family compositions can change, too, as sons and daughters need to help pay for and/or care for their older parents. This can lead to severe economic consequences as well. The family structures can change as well, as older individuals will often live by themselves or in group homes.
Economic Consequences
Lastly, there are economic consequences. With more older people and lower birth rates, you have fewer people in the workforce. This can lead to lower production, which will lead to less money being made. That is doubly bad when you consider how many people will have to use part of that money to care for elderly family members.
With the government spending more money on taking care of older people and healthcare, less money will be spent in other areas - education, technology, innovation, arts, etc.
Social security and pension systems are also affected as there is more pressure put on them. This can lead to a lot of debates on the sustainability of these systems and the possible need for reform.
🎥 Watch: AP HUG - Population Pyramids
Vocabulary
The following words are mentioned explicitly in the College Board Course and Exam Description for this topic.
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| aging population | A population with an increasing proportion of elderly individuals relative to younger age groups, resulting from declining birth rates and increasing life expectancy. |
| birth rate | The number of live births per unit of population (typically per 1,000 people) in a given time period; a key factor determining population aging. |
| death rate | The number of deaths per unit of population (typically per 1,000 people) in a given time period; a key factor determining population aging. |
| dependency ratio | The proportion of dependents (young and elderly) to working-age population; a measure of economic burden in aging societies. |
| life expectancy | The average number of years a person is expected to live from birth; influences the age structure of a population. |
Frequently Asked Questions
What is an aging population and why is it happening?
An aging population is when a country’s median age rises and a larger share of people are elderly (65+), usually shown by a top-heavy population pyramid and higher life expectancy. It happens because birth rates fall (often below replacement-level fertility ~2.1 children per woman) and death rates decline as healthcare and living standards improve—basically the late stages of the demographic transition. Policies (like China’s former one-child policy), greater female education and workforce participation, and better medical care speed this shift. Causes and consequences are exactly what the CED asks you to explain (SPS-2.C): economically it raises healthcare and pension spending and can shrink the labor force; socially it increases eldercare needs and can create ageism; politically it affects voting and public spending priorities. Also watch dependency ratio (more retirees per working-age person). For a focused review, see the topic study guide (https://library.fiveable.me/ap-human-geography/unit-2/aging-populations/study-guide/lOk6DoUdx37WCzGKPfvQ) and practice questions (https://library.fiveable.me/practice/ap-human-geography).
Why are birth rates and death rates important for understanding aging populations?
Birth and death rates (plus life expectancy) tell you how a population’s age structure changes over time—that’s the core of AP learning objective SPS-2.C. Low birth (fertility) rates—especially below replacement-level (~2.1 children per woman)—mean fewer young people entering the population. Low death rates and higher life expectancy push more people into older age groups. Together these shift the median age up, reshape the population pyramid into a top-heavy shape, and raise the dependency ratio (fewer working-age people per retired person). That creates economic and political consequences (higher healthcare and pension costs, eldercare needs, and possible labor shortages), which you need to explain on the exam. For examples and exact CED terms (dependency ratio, demographic transition, population pyramid), see the Topic 2.9 study guide (https://library.fiveable.me/ap-human-geography/unit-2/aging-populations/study-guide/lOk6DoUdx37WCzGKPfvQ). For unit review and extra practice problems, check Unit 2 (https://library.fiveable.me/ap-human-geography/unit-2) and the APHG practice set (https://library.fiveable.me/practice/ap-human-geography).
How does life expectancy affect whether a country has an aging population?
Higher life expectancy means more people survive to older ages, so the share of elderly (usually 65+) in the population rises. Per the CED, population aging is set by birth rates, death rates, and life expectancy (EK SPS-2.C.1). If life expectancy increases while fertility stays low (below replacement ~2.1), median age rises, the population pyramid narrows at the base, and the dependency ratio (nonworking elderly per working-age people) climbs—classic late stages of the demographic transition (think Japan, Germany, Italy). That creates economic and social effects: higher health care and pension costs, more long-term care demand, and political debates over social security (EK SPS-2.C.2). For more examples and AP-style practice, check the Topic 2.9 study guide (https://library.fiveable.me/ap-human-geography/unit-2/aging-populations/study-guide/lOk6DoUdx37WCzGKPfvQ), the Unit 2 overview (https://library.fiveable.me/ap-human-geography/unit-2), and practice questions (https://library.fiveable.me/practice/ap-human-geography).
What's the difference between aging populations in developed vs developing countries?
Developed countries: low fertility (often below replacement), high life expectancy, and older median ages—think Japan, Germany, Italy. That produces a high old-age dependency ratio, big pension and healthcare costs, more long-term care needs, and political pressure for immigration or policies to raise fertility. It’s a late-stage DTM pattern and shows up as top-heavy population pyramids. Developing countries: generally younger populations because fertility stayed higher and life expectancy rose more recently. Aging is slower, but some (e.g., China after the one-child policy) are rapidly aging with fewer resources. Consequences there include weaker pension systems, more informal eldercare (family-based), strain on healthcare without strong social security, and urban migration that can leave rural elders isolated. On the AP exam, link causes (fertility, mortality, life expectancy) to consequences like dependency ratio and economic/political impacts (EK SPS-2.C.1 & .2). For a quick topic review, see the Fiveable study guide (https://library.fiveable.me/ap-human-geography/unit-2/aging-populations/study-guide/lOk6DoUdx37WCzGKPfvQ), the unit overview (https://library.fiveable.me/ap-human-geography/unit-2), and practice questions (https://library.fiveable.me/practice/ap-human-geography).
Can someone explain what dependency ratio means in simple terms?
Dependency ratio is a simple way to measure how many people likely depend on the working population. You add the number of young people (usually ages 0–14) and older people (usually 65+) and divide by the number of working-age people (usually 15–64). Then multiply by 100 to get a percentage. So: (dependents ÷ working-age) × 100. If the ratio is high, each worker supports more dependents—more kids or more elderly—which stresses pensions, healthcare, and social services. An aging population raises the elderly share, so the dependency ratio goes up and can hurt the economy and public spending (CED keywords: dependency ratio, aging population, pension systems, healthcare expenditure). For AP review, see the Topic 2.9 study guide (https://library.fiveable.me/ap-human-geography/unit-2/aging-populations/study-guide/lOk6DoUdx37WCzGKPfvQ) and more unit resources (https://library.fiveable.me/ap-human-geography/unit-2). Practice problems: (https://library.fiveable.me/practice/ap-human-geography).
What are the main economic consequences when a country's population gets older?
When a country’s population ages (more people at 65+ and a higher median age), the main economic consequences are clear and tested on the AP: a higher dependency ratio, rising public spending on pensions and healthcare, and a shrinking labor force. That means slower GDP growth, higher taxes or bigger budget deficits to pay social security/pension systems, and more demand for long-term care and geriatric services. Employers may face labor shortages, prompting automation or policies to raise retirement ages, encourage immigration, or boost fertility. You’ll also see shifting consumption (more healthcare, less durable-goods spending) and political pressure over intergenerational equity—who pays for benefits. These points map directly to SPS-2.C in Topic 2.9 (see the Fiveable study guide for this topic: https://library.fiveable.me/ap-human-geography/unit-2/aging-populations/study-guide/lOk6DoUdx37WCzGKPfvQ). For more unit review and practice problems (1000+ Qs), check the unit page (https://library.fiveable.me/ap-human-geography/unit-2) and practice section (https://library.fiveable.me/practice/ap-human-geography).
How do aging populations affect politics and voting patterns?
An aging population changes politics because older people vote more, care more about pensions/healthcare, and thus shape policy priorities. Higher median age and a rising dependency ratio push governments to protect social security, increase healthcare spending, and consider pension reforms (EK SPS-2.C.2). Politically this often means stronger support for candidates/policies promising stable benefits, conservative spending on immigration, and slower change—though party effects vary by country. Aging electorates also boost influence of elder-focused interest groups and can create tensions in intergenerational equity (younger voters may push for education/affordable housing). Long-term consequences include fiscal strain (higher taxes or lower benefits) and policy shifts in countries like Japan, Germany, and Italy. Topic 2.9 is tested in Unit 2 on the AP exam, so study these political effects alongside demographic causes (EK SPS-2.C.1). For a focused review, use the Topic 2.9 study guide (https://library.fiveable.me/ap-human-geography/unit-2/aging-populations/study-guide/lOk6DoUdx37WCzGKPfvQ) and more practice problems at Fiveable (https://library.fiveable.me/practice/ap-human-geography).
I'm confused about how birth rates cause aging populations - shouldn't more births mean younger people?
You're right that more births mean more young people short-term—but population aging is about long-term age structure, not just yearly babies. An aging population happens when fertility (birth) rates fall below replacement level (about 2.1 children per woman) for many years while life expectancy rises. Fewer births mean smaller younger cohorts entering the population; at the same time people live longer, so older cohorts grow. That raises median age and the dependency ratio (more elderly dependents per working-age person). This is typical in late stages of the demographic transition and seen in Japan, Germany, Italy. For more AP-aligned detail on causes and consequences (life expectancy, fertility rate, dependency ratio), check the Topic 2.9 study guide (https://library.fiveable.me/ap-human-geography/unit-2/aging-populations/study-guide/lOk6DoUdx37WCzGKPfvQ) and practice problems (https://library.fiveable.me/practice/ap-human-geography).
What social problems happen when there are too many old people compared to young people?
When there are too many old people compared to young people (a high median age and rising dependency ratio), several social problems appear. Public pension and social security systems become strained as fewer workers pay taxes to support retirees, raising taxes or cutting benefits. Healthcare and long-term care demand spikes, increasing government and family costs for hospitals, eldercare, and specialized services. Labor shortages can slow economic growth and reduce services for everyone. Socially, ageism and intergenerational tension can grow if younger people feel unfairly burdened. Politically, older populations may push policies favoring pensions and healthcare over education or childcare. These are central consequences of aging populations in the CED (EK SPS-2.C.2). For more review, see the Topic 2.9 study guide (https://library.fiveable.me/ap-human-geography/unit-2/aging-populations/study-guide/lOk6DoUdx37WCzGKPfvQ) and extra practice (https://library.fiveable.me/practice/ap-human-geography).
How do I write an essay about the causes and consequences of aging populations?
Start with a clear thesis: explain aging populations result from low fertility/replacement-level fertility, higher life expectancy, and late stages of the demographic transition. In body paragraphs: 1) Causes—define fertility rate, life expectancy, median age, and use a population pyramid to show shrinking base; mention policies (e.g., one-child policy). 2) Economic consequences—explain rising dependency ratio, greater healthcare expenditure, pension strain, labor shortages. 3) Social/political consequences—eldercare demand, ageism, intergenerational equity, shifts in voting and policy. Use specific examples (Japan, Germany, Italy) and link causes to consequences with data. Conclude by summarizing impacts and suggesting policy responses (encourage fertility, immigration, pension reform, long-term care). On the AP FRQ, use precise CED terms (dependency ratio, demographic transition, replacement level) and label examples—aim for clear claims + evidence. For review and examples, see the Topic 2.9 study guide (https://library.fiveable.me/ap-human-geography/unit-2/aging-populations/study-guide/lOk6DoUdx37WCzGKPfvQ), the unit overview (https://library.fiveable.me/ap-human-geography/unit-2), and practice problems (https://library.fiveable.me/practice/ap-human-geography).
Why do some countries like Japan have such serious aging population problems?
Because birth rates fell below replacement (about 2.1 children per woman) and life expectancy rose, countries like Japan now have a high share of older adults and a high median age—classic late-stage demographic transition. Low fertility comes from urbanization, more women in the workforce, later marriage, and costs of raising kids (Japan also felt effects from past policies and social norms). Consequences match the CED: higher old-age dependency ratios strain pensions and social security, raise healthcare and long-term care spending, shrink the labor force, and shift politics toward elder-focused policies. Solutions used or discussed include raising retirement age, encouraging higher fertility with family benefits, promoting eldercare services, and selective immigration to increase working-age population. For a clear AP-aligned summary of causes and consequences (SPS-2.C), check the Topic 2.9 study guide (https://library.fiveable.me/ap-human-geography/unit-2/aging-populations/study-guide/lOk6DoUdx37WCzGKPfvQ) and practice more with Fiveable’s AP practice questions (https://library.fiveable.me/practice/ap-human-geography).
What happens to healthcare systems when populations age rapidly?
When populations age rapidly, healthcare systems face higher demand and bigger costs. Fewer working-age people raises the dependency ratio, so tax revenue for pensions, social security, and public health programs falls while healthcare expenditure and long-term care needs rise. You’ll see more chronic disease care, geriatric specialties, nursing-home demand, and home-based eldercare services. Systems often struggle with workforce shortages (fewer doctors, nurses, caregivers), longer wait times, and a shift from acute to ongoing care. Politically and economically this pressures budgets and can spark debates about intergenerational equity and pension reform (think Japan or Germany). For AP exam connections, link this to EK SPS-2.C.2 (dependency ratio, pension systems, healthcare expenditure) and be ready to explain causes/consequences on FRQs. For a quick refresher, check the Topic 2.9 study guide (https://library.fiveable.me/ap-human-geography/unit-2/aging-populations/study-guide/lOk6DoUdx37WCzGKPfvQ) and practice questions (https://library.fiveable.me/practice/ap-human-geography).
Compare the aging population issues in Europe versus Asia
Europe and Asia both face aging populations, but causes and consequences differ. Europe’s aging is mostly from long-term low fertility and high life expectancy (late stages of the demographic transition)—think Germany and Italy. Asia’s aging mixes low fertility plus past policy effects (e.g., China’s one-child policy) and very rapid aging in places like Japan. Consequences overlap: higher old-age dependency ratios, rising healthcare and long-term care costs, pension strain, labor shortages, and political pressure for immigration or pro-natalist policies. Differences: Europe generally has more developed social security and public eldercare systems but higher pension burdens and greater political debate over immigration; parts of Asia have weaker social safety nets, stronger family-based eldercare expectations, and faster demographic shifts that compress adaptation time. This fits Topic 2.9 (EK SPS-2.C.1–2) and is a common AP FRQ comparison. Review the study guide (https://library.fiveable.me/ap-human-geography/unit-2/aging-populations/study-guide/lOk6DoUdx37WCzGKPfvQ) and practice questions (https://library.fiveable.me/practice/ap-human-geography).
Does immigration help solve aging population problems or make them worse?
Short answer: Immigration helps, but it’s not a full fix. Why it helps: Immigrants are often working-age, so they lower the dependency ratio, add workers and taxpayers, and can ease pressure on pensions, healthcare, and labor shortages—useful short- to medium-term responses for aging countries like Japan or Germany (CED keywords: dependency ratio, fertility rate, life expectancy). Why it isn’t a complete solution: Immigrants age too, and fertility rates for immigrant groups often fall toward host-country levels over time. To fully offset low birth rates (below replacement ~2.1), countries need sustained, large inflows—politically and socially difficult to maintain. Immigration buys time and reduces economic strain but doesn’t fully reverse long-term population aging or higher median age. For AP prep: this topic fits EK SPS-2.C and could appear on FRQs about economic and social consequences of aging populations (see Fiveable study guide for Topic 2.9 (https://library.fiveable.me/ap-human-geography/unit-2/aging-populations/study-guide/lOk6DoUdx37WCzGKPfvQ) and more unit review (https://library.fiveable.me/ap-human-geography/unit-2). Practice applying this in questions at https://library.fiveable.me/practice/ap-human-geography.
What are the long-term effects of having more elderly people than working-age people in a country?
When a country has more elderly than working-age people, long-term effects hit the economy, society, and politics. Economically, the dependency ratio rises—fewer workers supporting more retirees—which strains pension systems, social security, and public budgets and can slow GDP growth. Healthcare and long-term care costs increase (higher life expectancy + low fertility). Socially, you get labor shortages, pressure to automate, ageism, and tougher intergenerational equity debates about taxes and benefits. Politically, governments may shift policy toward retirees (pensions, healthcare) and either restrict or expand immigration to fill jobs. Examples: Japan, Germany, Italy face these demographic-transition late-stage challenges. On the AP exam, you should be ready to explain causes (low fertility, higher life expectancy) and consequences (dependency ratio, pension stress, healthcare spending) using specific examples (CED keywords). For a quick review, see the Topic 2.9 study guide (https://library.fiveable.me/ap-human-geography/unit-2/aging-populations/study-guide/lOk6DoUdx37WCzGKPfvQ) and practice questions (https://library.fiveable.me/practice/ap-human-geography).