Von Thunen Model
The Von Thunen model is an economic model developed in the 19th century that aims to explain the spatial organization of agriculture and how it is influenced by transportation costs. The model was developed by Johann Heinrich von Thunen, a German economist and landowner.
According to the Von Thunen model, the spatial organization of agriculture is influenced by the distance of the farm from the market and the cost of transportation. Farms located closer to the market will be more profitable because they can sell their products at a higher price and have lower transportation costs. As a result, these farms will be more likely to produce high-value crops or livestock that are more profitable to sell.
On the other hand, farms located farther from the market will be less profitable because they have higher transportation costs and must sell their products at a lower price to compete with farms located closer to the market. These farms will be more likely to produce low-value crops or livestock that are less sensitive to price changes.
The Von Thunen model can be used to predict the spatial distribution of different types of agriculture and the relative profitability of different farming activities. It is a simplified model and does not take into account many real-world factors that can influence the spatial organization of agriculture, such as natural resources and infrastructure.
However, it remains an important conceptual model in economics and is often used to study the spatial organization of agriculture and other economic activities.
It predicts:
- More intensive rural land-uses closer to the marketplace
- Example: Commercial farming of milk (dairying)
- Farms locate closer to urban areas to minimize distance and lower transportation costs (otherwise, the milk will spoil)
- They don’t need as much space, so they can afford the higher price of land in regions closer to the market
- Example: Commercial farming of milk (dairying)
- More extensive rural land-uses further from the marketplace
- Example: Ranching
- Livestock need plenty of land to graze, so farmers occupied land further out, where there was a lot of it at a relatively low price.
- When the von Thunen Model was developed, the livestock were not killed until they reached the city market (so refrigeration/keeping the meat fresh wasn’t an issue)
- Example: Ranching
- *These rural land-use zones are represented by concentric rings in the model

Examples
Here are a few examples of how the Von Thunen model can be used to understand the spatial organization of agriculture:
- A farmer who grows high-value crops, such as vegetables or fruit, may choose to locate their farm closer to the market in order to take advantage of the higher prices and lower transportation costs.
- A farmer who raises livestock, such as cows or pigs, may choose to locate their farm farther from the market because the cost of transportation is a smaller proportion of the total cost of production. These farms may be more likely to produce lower-value products, such as feed grains, for the local market.
- A farmer who grows crops that are not perishable and can be stored for long periods of time, such as grains or oilseeds, may choose to locate their farm farther from the market in order to take advantage of lower land and labor costs. These crops can be transported over longer distances without spoiling, so the cost of transportation is less of a factor in their profitability.
- A farmer who grows crops that are perishable and must be sold soon after harvest, such as fresh vegetables or flowers, may choose to locate their farm closer to the market in order to reduce transportation costs and ensure that their products reach the market in good condition.
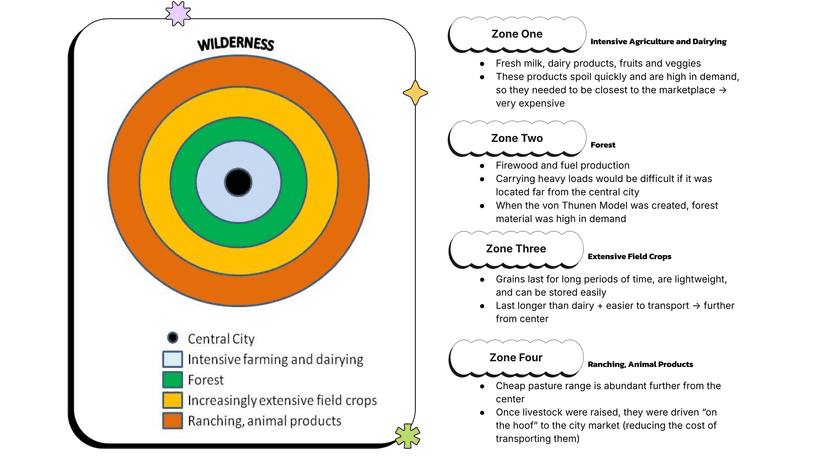
The Four Zones
There are four zones or concentric rings represented in the von Thunen Model, with the solid center core (not included as a ring) being the central city.
- Zone 1: Intensive agriculture and dairying
- Fresh milk, dairy products, certain fruits and vegetables
- These products spoil quickly and are high in demand, so they needed to be closest to the marketplace
- This farmland was high in demand (because of its accessibility) and very expensive as a result
- Zone 2: Forest
- Firewood and fuel production
- Carrying heavy loads would be difficult if it was located far from the central city
- When the von Thunen Model was created, forest material was high in demand for building and fuel (so it needed to get to the market quickly!)
- Zone 3: Extensive field crops
- This includes grains for bread (which require larger chunks of land for growing/harvesting)
- Grains last for long periods of time, are lightweight, and can be stored easily
- Situated further from the center because
- last longer than dairy products
- cheaper to transport than forest resources
- Zone 4: Ranching
- Cheap pasture range is abundant further from the center
- Once livestock were raised, they were driven “on the hoof” to the city market (reducing the cost of transporting them such a long distance)
Summary of Zones
In the Von Thunen model, agricultural land is divided into four zones based on the distance from the market and the cost of transportation. These zones are:
- The first (inner) zone: This is the most profitable zone because it is closest to the market and has the lowest transportation costs. Farms in this zone are likely to produce high-value crops or livestock that are sensitive to price changes, such as vegetables or fruit.
- The second (outer) zone: This zone is less profitable than the first zone because it is farther from the market and has higher transportation costs. Farms in this zone may produce lower-value crops or livestock that are less sensitive to price changes, such as feed grains or dairy products.
- The third (outer) zone: This zone is even less profitable than the second zone because it is even farther from the market and has even higher transportation costs. Farms in this zone may produce crops or livestock that are not as sensitive to price changes, such as livestock feed or lumber.
- The fourth (outer) zone: This is the least profitable zone because it is farthest from the market and has the highest transportation costs. Farms in this zone may produce crops or livestock that are not very sensitive to price changes, such as timber or timber products. It's important to note that the Von Thunen model is a simplified model and does not take into account many real-world factors that can influence the spatial organization of agriculture, such as natural resources and infrastructure. However, it remains an important conceptual model in economics and is often used to study the spatial organization of agriculture and other economic activities.
Assumptions
- The Von Thunen model is based on a number of assumptions, including:1. The cost of transportation is a linear function of distance: This means that the cost of transporting goods increases proportionally with distance.1. The market is located in the center of a circular agricultural region: This means that all farms are the same distance from the market.1. There is no transportation between different zones: This means that goods can only be transported between the farm and the market and not between farms in different zones.1. There are no externalities: This means that the production and transportation of goods has no impact on the environment or on other economic activities.1. Land is used solely for agricultural production: This means that there are no other land uses, such as urban development or recreation, that could affect the spatial organization of agriculture.1. There is a single dominant agricultural activity: This means that all farms in the region produce the same type of crop or raise the same type of livestock.These assumptions are simplifications of the real world and are not always accurate. However, the Von Thunen model remains a useful tool for understanding the spatial organization of agriculture and other economic activities.
🎥 Watch AP HUG - Spatial Organization
In Short
- Transportation costs determined agricultural activities and the spatial arrangement of them
- The Model = the center city and four concentric zones (the inner two are intensive, the outer two are extensive)
- Center City (solid core)
- Dairying and Intensive Agriculture
- Forest
- Extensive Field Crops
- Ranching
- Main assumptions for this model
- Flat land
- One centrally located city
- There are no disturbances to the economy
Important Part of Von Thunen Model
Here are some key points about the Von Thunen model:
- The Von Thunen model is an economic model developed in the 19th century that aims to explain the spatial organization of agriculture and how it is influenced by transportation costs.
- According to the Von Thunen model, the spatial organization of agriculture is influenced by the distance of the farm from the market and the cost of transportation.
- The Von Thunen model divides agricultural land into four zones based on distance from the market and the cost of transportation. The first (inner) zone is the most profitable because it is closest to the market and has the lowest transportation costs. The fourth (outer) zone is the least profitable because it is farthest from the market and has the highest transportation costs.
- The Von Thunen model is based on a number of assumptions, including that the cost of transportation is a linear function of distance, the market is located in the center of a circular agricultural region, there is no transportation between different zones, there are no externalities, land is used solely for agricultural production, and there is a single dominant agricultural activity.
- The Von Thunen model is a simplified model and does not take into account many real-world factors that can influence the spatial organization of agriculture. However, it remains an important conceptual model in economics and is often used to study the spatial organization of agriculture and other economic activities.
Vocabulary
The following words are mentioned explicitly in the College Board Course and Exam Description for this topic.
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| agricultural production | The cultivation and harvesting of crops and livestock for food and other products. |
| concentric rings | Circular zones of different agricultural land use patterns arranged around a central market in the von Thünen model. |
| distance from market | The spatial separation between agricultural production areas and the central market or urban center, which affects land use decisions. |
| rural land use | The patterns of how land in countryside and non-urban areas is utilized, including farming, forestry, and other agricultural activities. |
| specialty farming | Agricultural production focused on specific high-value crops or products rather than general subsistence or commodity farming. |
| transportation costs | The expenses associated with moving goods from their production location to the market, which increase with distance. |
| von Thünen model | A geographic model that explains rural land use patterns by analyzing how transportation costs and distance from the market influence the location and type of agricultural production. |
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the von Thünen model and why do we need to know it?
The von Thünen model is a geographic model that explains how different types of agriculture arrange themselves in concentric rings around a single market center based on transportation costs, perishability, and land value (bid-rent theory). Close to the market you find intensive, perishable products (market gardening, dairy); farther out are forests (for fuel), then grain, then ranching—because distance-decay raises transport costs and reduces what farmers can pay for land. You need to know it because the AP CED (PSO-5.D and EK PSO-5.D.1) expects you to explain how transportation costs shape rural land use at different scales and why real regions sometimes deviate from perfect rings (specialty farming, topography, multiple markets). The model shows key terms: concentric rings, intensive agriculture, perishability, bid rent. Review the topic study guide (https://library.fiveable.me/ap-human-geography/unit-5/von-thunen-model/study-guide/Yp98AboJ2DQWeTo9hDam) and try practice questions (https://library.fiveable.me/practice/ap-human-geography) to prep for multiple-choice and FRQ items.
How does the von Thünen model explain where farmers grow different crops?
The von Thünen model explains where farmers grow different crops by linking distance from a central market to transportation costs, perishability, and profit (bid rent theory). In the idealized model farmers form concentric rings around a market center: market gardening and dairy (highly perishable, intensive) are closest because they need quick delivery and pay higher rent; a forest ring provides wood (heavy, high transport cost); grain farming is farther out (less perishable, lower transport cost); and ranching/raising livestock occupies the outermost ring (extensive, low transport cost). The model shows distance-decay: as distance increases, farmers switch to lower-value, lower-transport-cost products. Remember: real regions often deviate—specialty farming, multiple markets, terrain, and modern transport/ refrigeration change patterns. Use this model to explain agricultural spatial organization on the AP exam (EK PSO-5.D.1). Review the topic study guide (https://library.fiveable.me/ap-human-geography/unit-5/von-thunen-model/study-guide/Yp98AboJ2DQWeTo9hDam) and unit overview (https://library.fiveable.me/ap-human-geography/unit-5) and practice questions (https://library.fiveable.me/practice/ap-human-geography).
Why are transportation costs so important in the von Thünen model?
Transportation costs are the key control in the von Thünen model because they determine how profitable different types of agriculture are as distance from the market increases. Goods that are perishable or expensive to move (like market gardening and dairy) need to be close to the market so transport time and cost stay low; less perishable, cheaper-to-ship products (like grain or ranching) can be produced farther away. This creates the model’s concentric rings and links to bid-rent theory: land closer to market has higher value for intensive, high-transport-cost uses. The model shows distance-decay in profit and spatial organization of land use, though real-world factors (terrain, roads, specialty farming) cause deviations. For AP exam prep, be ready to explain how transportation costs, perishability, and intensity of production shape the rings (see the Topic 5.8 study guide on Fiveable: https://library.fiveable.me/ap-human-geography/unit-5/von-thunen-model/study-guide/Yp98AboJ2DQWeTo9hDam) and practice with questions at (https://library.fiveable.me/practice/ap-human-geography).
What are the concentric rings in von Thünen's theory and what goes in each one?
Von Thünen pictured agricultural land as concentric rings around a single market. From the center outward: - Market/City (center)—where produce is sold. - Ring 1: Market gardening & dairy—intensive, perishable, high transport costs (vegetables, milk). - Ring 2: Forest/wood—bulky fuel and building materials (close enough to carry). - Ring 3: Grain/field crops—less perishable, grown on larger plots, lower transport cost per unit. - Ring 4: Ranching/animal grazing—extensive, needs lots of land, animals can be driven to market. The model explains spatial organization through transportation costs, bid-rent, and distance-decay: closer land supports high-value, intensive uses. Remember AP: use von Thünen to describe how transport costs shape land use (EK PSO-5.D.1), but real regions and specialty farming don’t always form perfect rings. For a quick review on this topic see the Fiveable study guide (https://library.fiveable.me/ap-human-geography/unit-5/von-thunen-model/study-guide/Yp98AboJ2DQWeTo9hDam) and try practice questions (https://library.fiveable.me/practice/ap-human-geography).
I'm confused about how distance from market affects what farmers grow - can someone explain this simply?
Think of the von Thünen model as a map of how transport costs and perishability decide what’s grown near a market. Close to the market you get intensive, high-value or perishable farming (market gardening, dairy) because short distance means low transport cost and fast delivery. A bit farther out, less-perishable but still valuable crops (like grains) appear—they need more land but tolerate travel. Farthest are extensive, low-value uses (ranching) because long transport makes cheap, bulky products economical only with lots of space. This idea uses bid-rent (land closer to market is more valuable) and distance-decay (value drops with distance). Remember: von Thünen assumes one market, flat land, and uniform transport—real regions (specialty farming, roads, government policy) often break the neat rings. For AP exam relevance, this is PSO-5.D (expect MCQs and FRQ links to transport costs and land-use patterns). Review the topic guide (https://library.fiveable.me/ap-human-geography/unit-5/von-thunen-model/study-guide/Yp98AboJ2DQWeTo9hDam) and practice questions (https://library.fiveable.me/practice/ap-human-geography).
What's the difference between the von Thünen model and other agricultural location theories we've learned?
Von Thünen is specifically about how distance from a single market shapes rural land use: higher-value, perishable, or land-intensive products (market gardening, dairy, forests for fuel) cluster close to the market because transportation costs and perishability raise costs with distance; lower-value, less perishable uses (grain, ranching) locate farther out. That emphasis on transportation costs and concentric rings (bid-rent logic) is what makes it different from other agricultural ideas you’ve seen. Compare that to other theories: bid-rent is more general about how land value falls with distance (applies to urban land too); Boserup focuses on population-driven agricultural intensification (technology/social response), not spatial cost; origin/diffusion models explain where farming began, not where it sits relative to a market. For the AP exam, von Thünen helps you explain spatial organization and distance-decay effects (PSO-5.D, EK PSO-5.D.1). Review the topic study guide (https://library.fiveable.me/ap-human-geography/unit-5/von-thunen-model/study-guide/Yp98AboJ2DQWeTo9hDam) and practice questions (https://library.fiveable.me/practice/ap-human-geography).
How do I write an FRQ about the von Thünen model and agricultural land use patterns?
Start with a quick thesis that answers the prompt (e.g., “Von Thünen explains agricultural land use by linking transportation costs and distance from a market; I will describe the model, apply it to place(s), and note exceptions.”). Then follow this 3-part structure for a 7-point FRQ: 1) Define and describe (1–2 sentences): Define the Von Thünen model, concentric rings, market center, transportation costs, and bid-rent theory (use CED terms: intensive agriculture, market gardening, dairy, forest, grain, ranching, perishability, distance-decay). 2) Apply/Explain (2–3 sentences): Use the model to explain why high-value, perishable goods locate closest to market (market gardening/dairy), mid-distance is grain, outermost is ranching—tie each ring to transportation cost and perishability. Show you can do this at multiple scales (local city market vs. regional export). 3) Limitations & real-world example (1–2 sentences): Mention specialty farming, transportation tech, government policy, or landforms that break concentric rings and give a concrete example. Use task verbs from the exam (describe, explain, compare). Practice writing one timed response using the von Thünen study guide (https://library.fiveable.me/ap-human-geography/unit-5/von-thunen-model/study-guide/Yp98AboJ2DQWeTo9hDam) and more practice questions (https://library.fiveable.me/practice/ap-human-geography).
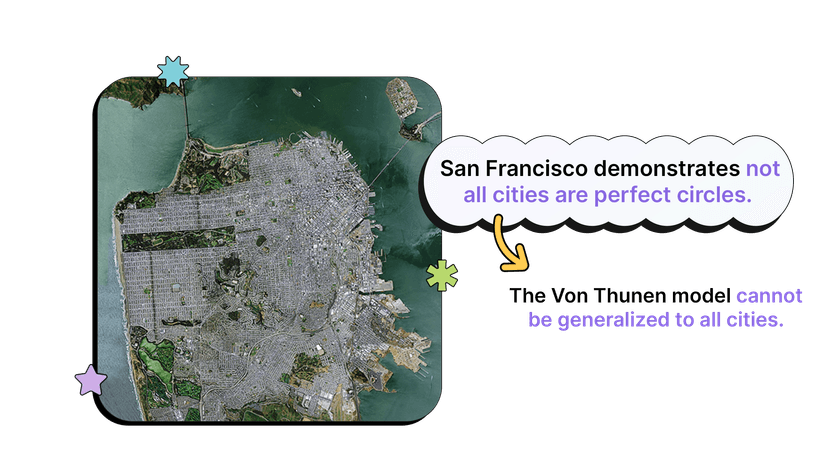
Why doesn't the von Thünen model work perfectly in real life situations?
The von Thünen model is super useful for showing how transportation costs and distance from a market shape land use (EK PSO-5.D.1), but it doesn’t match reality because its assumptions are too simple. Real places don’t have a single isolated market or a flat, uniform landscape—there are multiple cities, rivers, roads, mountains, and different soils and climates. Technology, refrigerated transport, and improved roads lower shipping costs so perishability matters less. Government policies, land ownership, and specialty farming also change where things locate. In short: bid-rent and distance-decay are real ideas, but real-world factors (topography, multiple markets, transportation tech, and cultural or economic differences) break the neat concentric rings. For a clear AP-focused summary, see the Fiveable Von Thünen study guide (https://library.fiveable.me/ap-human-geography/unit-5/von-thunen-model/study-guide/Yp98AboJ2DQWeTo9hDam). For extra practice, try the AP Human Geo question bank (https://library.fiveable.me/practice/ap-human-geography).
What are some examples of specialty farming that don't fit the von Thünen rings?
Classic examples: plantation agriculture (tropical cash crops like bananas, coffee, rubber) and Mediterranean specialty crops (olives, grapes, citrus) don’t fit neat von Thünen rings because they depend on climate, colonial trade patterns, or niche markets more than simple distance-to-market. Also: high-value perishables grown in greenhouses or vertical farms located inside/near cities; specialty dairy and artisan cheese producers who cluster near processing facilities; luxury horticulture (cut flowers, nursery plants) that uses cold-chain logistics and air freight to serve distant markets; and export-oriented agribusiness (soy, palm oil) located where climate and land availability matter, not market distance. These cases show how perishability, transportation tech (bid-rent), climate, and global demand distort the concentric-ring pattern in the CED (EK PSO-5.D.1). For a quick AP-aligned review, see the von Thünen study guide (https://library.fiveable.me/ap-human-geography/unit-5/von-thunen-model/study-guide/Yp98AboJ2DQWeTo9hDam). For wider Unit 5 review and extra practice, check the unit page (https://library.fiveable.me/ap-human-geography/unit-5) and practice problems (https://library.fiveable.me/practice/ap-human-geography).
How does modern transportation technology affect the von Thünen model today?
Modern transportation technology reduces the role of distance in von Thünen’s model by lowering transportation costs and shrinking perishability constraints. Things like refrigerated trucks, container shipping, high-speed rail, and air freight let perishable goods (dairy, vegetables, flowers) be produced farther from market than von Thünen predicted, so the neat concentric rings often break into scattered specialty-farming zones. GPS, better roads, and just-in-time logistics also change bid-rent calculations—land farther from the market can be profitable because shipping is cheaper and faster. For the AP exam, you should be able to describe how transportation advances change spatial organization at different scales (local, regional, global) and why real-world patterns don’t always match the concentric rings (CED EK PSO-5.D.1: transportation costs, perishability, bid rent). Review the topic study guide (https://library.fiveable.me/ap-human-geography/unit-5/von-thunen-model/study-guide/Yp98AboJ2DQWeTo9hDam) and practice questions (https://library.fiveable.me/practice/ap-human-geography) to see examples and FRQ-style applications.
What happens to agricultural production patterns when you move farther away from the central market?
As you move farther from the central market, agricultural production shifts because transportation costs and perishability matter—this is the core of von Thünen’s model (concentric rings, bid-rent theory). Close to the market you’ll find intensive, high-value, perishable products (market gardening, dairy) because farmers pay higher rent to be near buyers. A bit farther out is a forest zone (historically for fuel/wood), then semi-intensive grain farming (less perishable, lower transport cost), and finally extensive ranching/livestock on the outermost ring where land is cheapest. Distance-decay of profits explains the spatial organization. Remember: real regions don’t always make perfect rings (specialty farming and infrastructure alter patterns). For the AP exam, link this explanation to transportation costs and land-use patterns (Topic 5.8). Review the Fiveable study guide for von Thünen (https://library.fiveable.me/ap-human-geography/unit-5/von-thunen-model/study-guide/Yp98AboJ2DQWeTo9hDam) and try practice questions (https://library.fiveable.me/practice/ap-human-geography).
Can the von Thünen model be applied to different scales like local farms vs entire countries?
Short answer: Yes—the von Thünen model can be applied at different scales, but you must tweak expectations. Why: von Thünen explains how transportation costs and distance from a market shape land use (bid rent theory, concentric rings: market gardening/dairy close in, grain and ranching farther out). That logic works for a single local market (a town and surrounding farms) and can also help explain national or regional patterns when you treat big cities or ports as markets. Limitations: the model is idealized (EK PSO-5.D.1). Real places have multiple markets, roads, rail, perishability, topography, policy, and technology that break the neat rings. Specialty farming, global trade, and modern transport move intensive agriculture farther from markets. For AP prep: Unit 5 is tested 12–17% of the exam and scale analysis appears on multiple-choice and FRQs (scale skill weighting ~13–20%), so practice applying von Thünen at local and regional scales (see the Topic 5.8 study guide: https://library.fiveable.me/ap-human-geography/unit-5/von-thunen-model/study-guide/Yp98AboJ2DQWeTo9hDam). More practice problems: https://library.fiveable.me/practice/ap-human-geography
I missed class - what's this whole thing about concentric circles and farming?
Think of Von Thünen as a simple model that explains why different farms form rings around a single market based on transportation cost and perishability. Closest to the market you get intensive, high-value or perishable products (market gardening, dairy) because quick delivery matters and land is expensive. A little farther out you’d find wood/forest (historically for fuel), then extensive crops like grain, and farthest is ranching—low-value, land-hungry activities. The model uses bid-rent ideas: farmers nearer the market can pay more for land because they save on transport. On the AP exam, you should be able to describe the model, link it to transportation costs/distance-decay, and note limits—real regions have multiple markets, roads, terrain, and specialty farming so concentric rings don’t always match reality (CED EK PSO-5.D.1). Review the topic guide on Fiveable for a clear diagram and examples (https://library.fiveable.me/ap-human-geography/unit-5/von-thunen-model/study-guide/Yp98AboJ2DQWeTo9hDam) and try practice questions (https://library.fiveable.me/practice/ap-human-geography).
How do cultural practices mess up the von Thünen model predictions?
Von Thünen predicts concentric rings based on transportation cost, perishability, and bid-rent, but cultural practices change real outcomes. For example, dietary preferences or religious food rules concentrate certain crops far from market (tea in South Asia, halal markets), communal land-tenure or inheritance can keep small farms near or far from cities, and terrace/irrigation farming in mountains breaks the flat-land assumption. Seasonal festivals or cultural demand for specialty products (spices, heirloom vegetables) create pockets of intensive farming away from predicted rings. Pastoral nomadism and transhumance move livestock seasonally, so ranching isn’t a simple outer ring. These human choices violate von Thünen’s assumptions (isolated state, uniform land, single market), so regions of specialty farming don’t always match concentric rings (EK PSO-5.D.1). For a quick review, check the Topic 5.8 study guide (https://library.fiveable.me/ap-human-geography/unit-5/von-thunen-model/study-guide/Yp98AboJ2DQWeTo9hDam) and try practice questions (https://library.fiveable.me/practice/ap-human-geography).
What are the long-term effects of following von Thünen principles on rural land use?
If farmers consistently follow von Thünen principles long-term, rural land use tends to organize by distance-related cost and value: high-value, perishable, labor-intensive crops and dairy cluster close to the market; timber and less-intensive grain/ranching locate farther out (concentric rings driven by transportation costs and bid-rent). Over decades this produces land-value gradients, specialization of zones, and more intensive land use near cities. But changes in technology, cheaper transport, or new markets can break the rings—leading to consolidation into larger farms, monoculture in outer zones, or conversion of nearby farmland to suburban development (distance-decay weakens). Environmental effects include loss of biodiversity near specialized areas and soil depletion from continuous intensive use. For the AP exam, be ready to describe how von Thünen explains spatial organization and when regions won’t fit the model (PSO-5.D). Review the topic study guide (https://library.fiveable.me/ap-human-geography/unit-5/von-thunen-model/study-guide/Yp98AboJ2DQWeTo9hDam) and practice questions (https://library.fiveable.me/practice/ap-human-geography).