The Big Takeaway Of This Unit
Recursion We can use recursion in order to simplify repeated codes and loops.
Unit Overview
Exam Weighting
- 5-7.5% of the test
- Roughly 2 to 3 multiple-choice questions
Enduring Understanding
Sometimes, you can break down a large problem or task by doing a subproblem repeatedly. This is called recursion. If this sounds like loops and iteration, it's because all recursive (the adjective form of recursion) methods can be written as a loop! We will learn how to use recursion effectively and see how this will simplify our code!
Building Computational Thinking
When writing recursion, notice how the code is much more simplified than if we were using loops. But, they will run slower, so we will sacrifice speed for conciseness in code. Recursive code has two main parts, the repeating/recursive part and the base case which makes sure we don't create an infinite loop in which our programs never stop.
Main Ideas for This Unit
- Intro to Recursion
- How to code recursive methods
- Recursive Algorithms
10.1: Recursion
Intro to Recursion
Recursion is a way to simplify problems by having a subproblem that calls itself repeatedly. A recursive method has two parts: a base case and the recursive call. In the recursive call, the method basically calls itself, telling it to start over, either with the same parameters or different ones. After multiple calls, we approach the base case, where the recursion is stopped.
Here is its anatomy:
public static void recursiveMethod()
if (baseCaseCondition) { // base case
base case steps
} else {
do something
recursiveMethod(); // recursive call
}
}
The Base Case
The base case is the last recursive call. When the base case is reached, the recursion is stopped and a value is returned. The base case is the easiest part of the recursive call to write and should be written first to make sure that the program doesn't run forever.
Recursive Calls and the Call Stack
The recursive calls are the different calls to the method. Each of the different recursive calls has different parameter values and leads up to the base case being reached. To write efficient recursion, recognize what the subtask is and what is different between each time the subtask is done. The subtask is the recursive call and what is different and stays the same are the parameters.
Whenever we have a recursive method, we have a call stack that keeps track of all the times that the recursive function is called, as well as their individual parameters. This is useful for when we have a function that has a recursive call in its return statement where the results of later recursive calls are used in past calls. Here is a picture demonstrating the call stack for recursion.
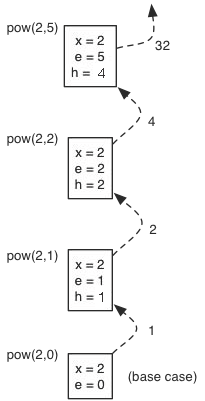
Courtesy of Cornell University.
In this, x and e are the parameters of the recursive calls, and h is the result of the recursion that is passed back up. The recursive calls are made from top to bottom, while the recursive returns are passed from bottom to top. This is where tracing comes in handy, as shown in the picture above!
Recursion vs. Loops
All recursion can be written as a loop, that is, all recursive code can be written iteratively. If we can just use iteration, why use recursion? The main answer? Simplicity. Recursive code is usually easier to read than iterative code. Is there a trade-off? Yes. This comes in the form of speed and memory. This is because the call stack takes up memory in your computer when running the program, and it takes time to pass up the recursive return values.
Here is an example of an iterative and recursive method to do multiplication using repeated addition:
Iterative Code:
public static int multiply(int a, int b) {
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < b; i++) {
sum += a;
}
return sum;
}
Recursive Code
public static int multiply(int a, int b) {
if (b == 0) {
return 0;
} else {
return multiply(a, b - 1) + a;
}
}
On the AP test FRQs, you can choose whether to write code iteratively or recursively, but you still have to know how recursion works for the AP exam!
Recursive Traversals
We can write ArrayList traversal using recursion. As a reminder, here is the iterative code:
for (int i = 0; i < arrayList.size(); i++) {
System.out.println(arrayList);
}
Meanwhile, here is the recursive code:
public static void traverseArray(ArrayList<Integer> array, int startIndex) {
if (startIndex == array.size() - 1) { // base case
System.out.println(array.get(0));
} else { // recursive case
System.out.println(array.subList(startIndex, array.size()).get(0));
traverseArray(array, startIndex + 1)
}
}
//to use the above method
traverseArray(array, 0)
What This Method Is Doing
The recursion is actually getting the sublist of the big ArrayList with the first item in the sublist acting as the next item to be printed, and the last item in the sublist acts as the last item in the ArrayList. The base case is when there is only one item left in the sublist, at which point the last item is printed and the method stopped.


