
Greenhouse Gases
4 min read•november 23, 2021
Sitara H
Sitara H
Humans have altered natural atmospheric concentrations of gasses increasing global temperatures.
On the simplest level, a “greenhouse gas” is any gas with the ability to trap heat waves (in the form of the Sun’s radiation) in the Earth’s atmosphere. With that definition in mind, let's dig deeper! 🌞
Types of Greenhouse Gases
The most common greenhouse gases are Carbon Dioxide (CO2), Methane (CH4), and Nitrous Oxide (N2O, also known as "laughing gas"). 😲
While carbon production is natural by default, human industrial activities like deforestation and the burning of fossil fuels have contributed more to accelerating global warming. 🔥
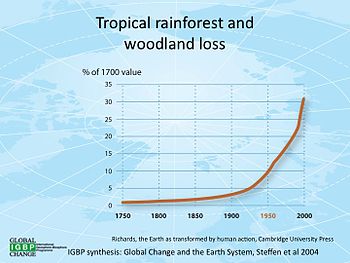
This data covers up to 2004. Think about the rate of forest loss TODAY!
Image courtesy of Wikipedia
In contrast, the vast majority of methane production comes from plant and animal agriculture. While the amount of methane produced annually is less than that of carbon dioxide, methane is more dangerous as it has more than 80 times the warming power that carbon dioxide does. 🐄
Nitrous oxide, similarly to methane, is mostly produced from various agricultural activities like the excessive use of fertilizers and the burning of agricultural residue. 🌱
Ozone
While ozone (O3) is technically classified as a greenhouse gas, it can be helpful or harmful to the planet depending on where in the atmosphere it is found. The gas occurs naturally at higher elevations, such as in the stratosphere where it forms a protective layer for the planet that blocks harmful UV radiation from reaching plants and animals.
Image courtesy of Wikipedia
What Creates Greenhouse Gases?
A small number of greenhouse gases have always been present in Earth’s atmosphere. Still, over the last 150 years (since the Industrial Revolution of the late 1700s), the quantity has dramatically increased due almost entirely to human industrial activity. 🚬
At least in the United States (as of 2005), 14.3% of greenhouse gas emissions are from the transportation sector. A whopping 25% is from the production of electricity, which includes burning coal and natural gas. Other significant contributors to the production of gases include agriculture and other industrial processes. ⚡
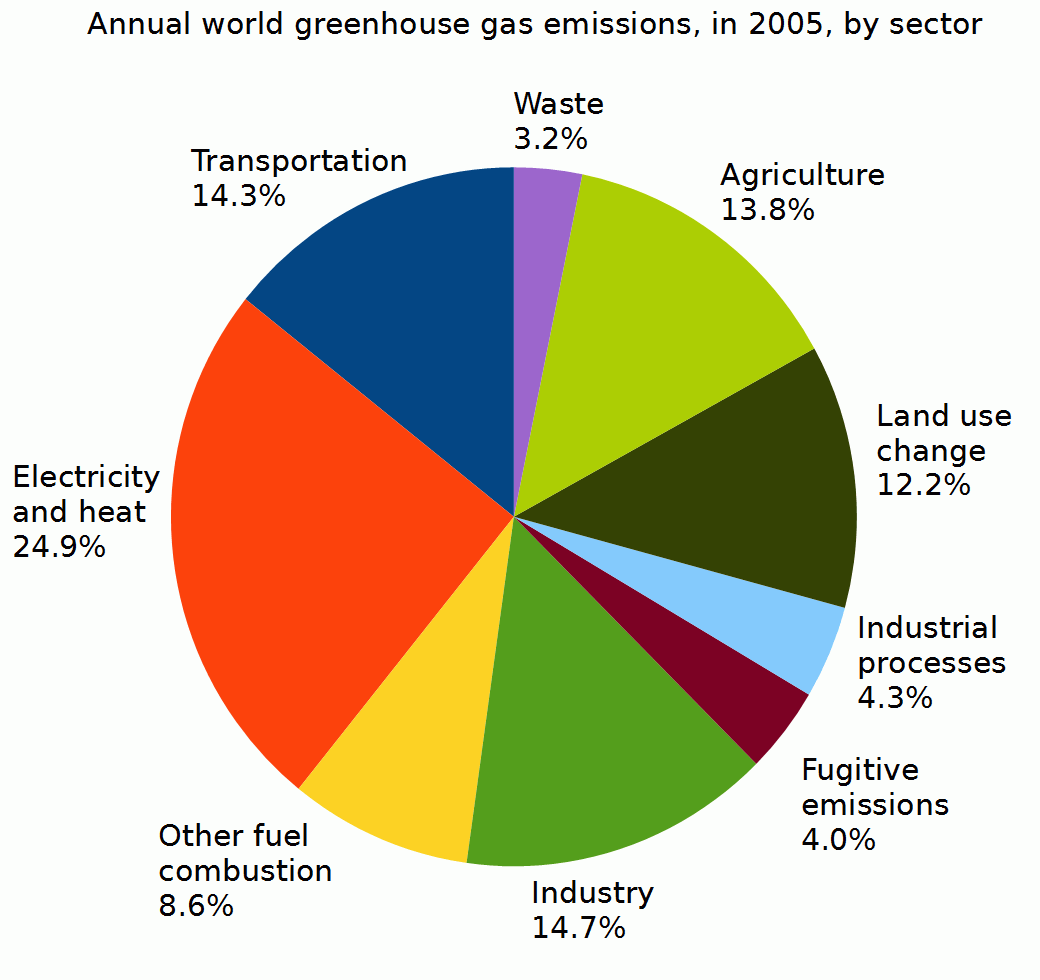
Image courtesy of Wikimedia
Effects of Greenhouse Gases
Global Warming
As it is known, the greenhouse effect occurs because the Sun emits lots of radiation in the form of heat towards Earth. However, only about 70% is absorbed on Earth, and the remaining radiation is reflected back to space. Where greenhouse gases come in, though, is when they trap some of the radiation that the Earth tries to reflect, heating up the Earth’s atmosphere. 🖼
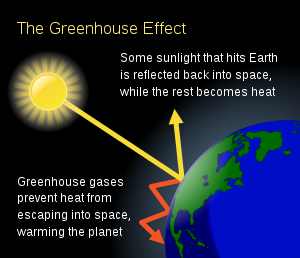
Image courtesy of Wikipedia
Over time, as the presence of such gases increases in Earth’s atmosphere, the planet gradually heats up in the process known as global warming. 📈
Rising Sea Levels
Another effect of increased greenhouse gases in the atmosphere goes hand in hand with global warming: the gradual rise in sea levels. The gases trap the Sun’s radiation inside Earth’s atmosphere, which causes the glaciers in polar regions to melt due to increasing temperatures. 🧊
Many scientists predict that if our emissions stay at the same rate and global warming continues the way it is now, Earth’s sea levels will rise by multiple inches in the next few decades. Let that idea sink in. ✖
Biological Cycles
Because the atmosphere is becoming warmer over time due to greenhouse gases trapping the Sun’s UV radiation, evaporation rates are also increasing. Therefore, the expected amount of rain will keep increasing, as per the water cycle. This also means that increased precipitation rates can cause soil erosion and reduced oxygen in the soil, harming plants and Earth's biodiversity as a whole. 🌂
Trends Over Time
In general, global warming works because greenhouse gases trap more heat in Earth’s atmosphere than would be present otherwise and contribute to the overall warming of the planet. 🌐
Since 1990, gross greenhouse gases emissions have risen by an average of 2 percent. However, in 2019, there was a decrease in emissions compared to 2018, which can be attributed to a decrease in total energy use and a trend towards the usage of more renewable energy sources than fossil fuels. 📉
Our emissions have many adverse effects on Earth’s climate and biodiversity; the increased heat in the atmosphere accelerates the process of global warming, simultaneously causing a rise in sea levels. In addition, the increased precipitation caused by disruptions in the water cycle can lead to rare events like soil erosion, which can ruin biodiversity in many places, becoming more commonplace. 🌳
Sources for Additional Reading
“Sources of Greenhouse Gas Emissions,” EPA (Environmental Protection Agency), accessed October 25, 2021, https://www.epa.gov/ghgemissions/sources-greenhouse-gas-emissions.
🤝Connect with other students studying greenhouse gases with Hours.
Greenhouse Gases
4 min read•november 23, 2021
Sitara H
Sitara H
Humans have altered natural atmospheric concentrations of gasses increasing global temperatures.
On the simplest level, a “greenhouse gas” is any gas with the ability to trap heat waves (in the form of the Sun’s radiation) in the Earth’s atmosphere. With that definition in mind, let's dig deeper! 🌞
Types of Greenhouse Gases
The most common greenhouse gases are Carbon Dioxide (CO2), Methane (CH4), and Nitrous Oxide (N2O, also known as "laughing gas"). 😲
While carbon production is natural by default, human industrial activities like deforestation and the burning of fossil fuels have contributed more to accelerating global warming. 🔥

This data covers up to 2004. Think about the rate of forest loss TODAY!
Image courtesy of Wikipedia
In contrast, the vast majority of methane production comes from plant and animal agriculture. While the amount of methane produced annually is less than that of carbon dioxide, methane is more dangerous as it has more than 80 times the warming power that carbon dioxide does. 🐄
Nitrous oxide, similarly to methane, is mostly produced from various agricultural activities like the excessive use of fertilizers and the burning of agricultural residue. 🌱
Ozone
While ozone (O3) is technically classified as a greenhouse gas, it can be helpful or harmful to the planet depending on where in the atmosphere it is found. The gas occurs naturally at higher elevations, such as in the stratosphere where it forms a protective layer for the planet that blocks harmful UV radiation from reaching plants and animals.

Image courtesy of Wikipedia
What Creates Greenhouse Gases?
A small number of greenhouse gases have always been present in Earth’s atmosphere. Still, over the last 150 years (since the Industrial Revolution of the late 1700s), the quantity has dramatically increased due almost entirely to human industrial activity. 🚬
At least in the United States (as of 2005), 14.3% of greenhouse gas emissions are from the transportation sector. A whopping 25% is from the production of electricity, which includes burning coal and natural gas. Other significant contributors to the production of gases include agriculture and other industrial processes. ⚡

Image courtesy of Wikimedia
Effects of Greenhouse Gases
Global Warming
As it is known, the greenhouse effect occurs because the Sun emits lots of radiation in the form of heat towards Earth. However, only about 70% is absorbed on Earth, and the remaining radiation is reflected back to space. Where greenhouse gases come in, though, is when they trap some of the radiation that the Earth tries to reflect, heating up the Earth’s atmosphere. 🖼

Image courtesy of Wikipedia
Over time, as the presence of such gases increases in Earth’s atmosphere, the planet gradually heats up in the process known as global warming. 📈
Rising Sea Levels
Another effect of increased greenhouse gases in the atmosphere goes hand in hand with global warming: the gradual rise in sea levels. The gases trap the Sun’s radiation inside Earth’s atmosphere, which causes the glaciers in polar regions to melt due to increasing temperatures. 🧊
Many scientists predict that if our emissions stay at the same rate and global warming continues the way it is now, Earth’s sea levels will rise by multiple inches in the next few decades. Let that idea sink in. ✖
Biological Cycles
Because the atmosphere is becoming warmer over time due to greenhouse gases trapping the Sun’s UV radiation, evaporation rates are also increasing. Therefore, the expected amount of rain will keep increasing, as per the water cycle. This also means that increased precipitation rates can cause soil erosion and reduced oxygen in the soil, harming plants and Earth's biodiversity as a whole. 🌂
Trends Over Time
In general, global warming works because greenhouse gases trap more heat in Earth’s atmosphere than would be present otherwise and contribute to the overall warming of the planet. 🌐
Since 1990, gross greenhouse gases emissions have risen by an average of 2 percent. However, in 2019, there was a decrease in emissions compared to 2018, which can be attributed to a decrease in total energy use and a trend towards the usage of more renewable energy sources than fossil fuels. 📉
Our emissions have many adverse effects on Earth’s climate and biodiversity; the increased heat in the atmosphere accelerates the process of global warming, simultaneously causing a rise in sea levels. In addition, the increased precipitation caused by disruptions in the water cycle can lead to rare events like soil erosion, which can ruin biodiversity in many places, becoming more commonplace. 🌳
Sources for Additional Reading
“Sources of Greenhouse Gas Emissions,” EPA (Environmental Protection Agency), accessed October 25, 2021, https://www.epa.gov/ghgemissions/sources-greenhouse-gas-emissions.
🤝Connect with other students studying greenhouse gases with Hours.

Resources
© 2024 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.
AP® and SAT® are trademarks registered by the College Board, which is not affiliated with, and does not endorse this website.