
2.4 Price Elasticity of Supply
2 min read•november 14, 2020
Jeanne Stansak
Jeanne Stansak
Unit 2: Supply and Demand
2.4: Price Elasticity of Supply
Definition
The is the measurement of how responsive firms (businesses) are to a change in the price of a good or service in the market. It shows us just how much they will alter their production when the price of a product changes.
💡You must drop all negatives when calculating the elasticity of supply.
Types of Elasticity
Just like with demand, there are 3 types of elasticity for supply: elastic, inelastic, and :
- Elastic supply means that firms are very responsive to price changes (i.e. if the price of a product increases there will be a large increase in the quantity supplied).
- Inelastic supply means that firms are not very responsive to price changes (i.e. if the price of a product increases, there will be a small increase in the quantity supplied).
- means that firms are proportionally responsive to changes in market price (i.e. if there is a 30% increase in price then there will be a 30% increase in quantity supplied).
Time is the biggest factor in determining the . Producers need time to adjust production or retrieve the resources needed for production. Most goods have an inelastic supply in the (where at least one resource is fixed) and have an elastic supply in the . Sometimes, you will have a which means that the quantity of goods is set and cannot be changed (i.e. there are a set number of hotel rooms in a hotel 🏨).
Resources are typically fixed in the short run because producers are not able to acquire new resources or change the number of resources they have that quickly. Let's consider this scenario, a farmer has 10 acres on which he grows oranges and learns that he can get a higher price for oranges at the market. His first reaction is to produce more oranges however he is limited to the 10 acres of land. This is an example of being in the short run. As more time passes he may be able to acquire additional acreage of land, and be operating in the long run.🍊
Calculating the Price Elasticity of Supply
Formula:
Remember to drop the negatives when solving for elasticity of supply!

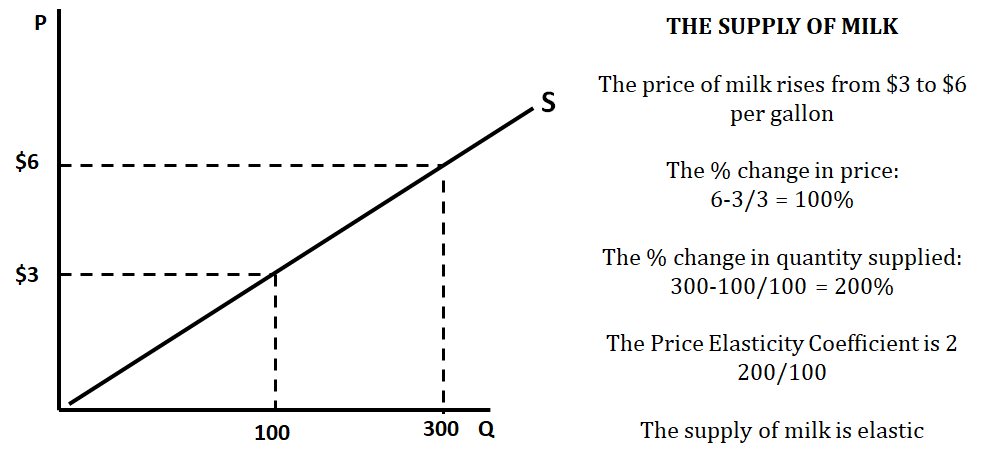
Rules:
The elasticity coefficient you just calculated can be applied to determine the type of supply for that good or service.
Key Terms to Review (5)
Long-run
: The long-run refers to a period of time during which all factors of production can be adjusted. Firms have more flexibility in this timeframe and can make changes such as expanding their factory size or hiring more workers.Perfectly Inelastic Supply
: Perfectly inelastic supply refers to a situation where the quantity supplied does not respond at all to changes in price. In other words, no matter how much the price changes, the quantity supplied remains constant.Price Elasticity of Supply
: Price elasticity of supply measures the responsiveness of quantity supplied to a change in price. It shows how sensitive producers are to changes in price.Short-run
: The short-run refers to a period of time in which at least one input is fixed, meaning it cannot be changed. This can range from a few months to a year.Unit Elastic
: Unit elastic refers to a situation where the percentage change in quantity demanded or supplied is equal to the percentage change in price. In other words, when the price changes by a certain percentage, the quantity demanded or supplied changes by an equal percentage.2.4 Price Elasticity of Supply
2 min read•november 14, 2020
Jeanne Stansak
Jeanne Stansak
Unit 2: Supply and Demand
2.4: Price Elasticity of Supply
Definition
The is the measurement of how responsive firms (businesses) are to a change in the price of a good or service in the market. It shows us just how much they will alter their production when the price of a product changes.
💡You must drop all negatives when calculating the elasticity of supply.
Types of Elasticity
Just like with demand, there are 3 types of elasticity for supply: elastic, inelastic, and :
- Elastic supply means that firms are very responsive to price changes (i.e. if the price of a product increases there will be a large increase in the quantity supplied).
- Inelastic supply means that firms are not very responsive to price changes (i.e. if the price of a product increases, there will be a small increase in the quantity supplied).
- means that firms are proportionally responsive to changes in market price (i.e. if there is a 30% increase in price then there will be a 30% increase in quantity supplied).
Time is the biggest factor in determining the . Producers need time to adjust production or retrieve the resources needed for production. Most goods have an inelastic supply in the (where at least one resource is fixed) and have an elastic supply in the . Sometimes, you will have a which means that the quantity of goods is set and cannot be changed (i.e. there are a set number of hotel rooms in a hotel 🏨).
Resources are typically fixed in the short run because producers are not able to acquire new resources or change the number of resources they have that quickly. Let's consider this scenario, a farmer has 10 acres on which he grows oranges and learns that he can get a higher price for oranges at the market. His first reaction is to produce more oranges however he is limited to the 10 acres of land. This is an example of being in the short run. As more time passes he may be able to acquire additional acreage of land, and be operating in the long run.🍊
Calculating the Price Elasticity of Supply
Formula:
Remember to drop the negatives when solving for elasticity of supply!


Rules:
The elasticity coefficient you just calculated can be applied to determine the type of supply for that good or service.
Key Terms to Review (5)
Long-run
: The long-run refers to a period of time during which all factors of production can be adjusted. Firms have more flexibility in this timeframe and can make changes such as expanding their factory size or hiring more workers.Perfectly Inelastic Supply
: Perfectly inelastic supply refers to a situation where the quantity supplied does not respond at all to changes in price. In other words, no matter how much the price changes, the quantity supplied remains constant.Price Elasticity of Supply
: Price elasticity of supply measures the responsiveness of quantity supplied to a change in price. It shows how sensitive producers are to changes in price.Short-run
: The short-run refers to a period of time in which at least one input is fixed, meaning it cannot be changed. This can range from a few months to a year.Unit Elastic
: Unit elastic refers to a situation where the percentage change in quantity demanded or supplied is equal to the percentage change in price. In other words, when the price changes by a certain percentage, the quantity demanded or supplied changes by an equal percentage.
Resources
© 2024 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.
AP® and SAT® are trademarks registered by the College Board, which is not affiliated with, and does not endorse this website.